CNC Machining Titanium Parts

Titanium materials are materials with certain shapes, sizes, and performances made of titanium ingots and titanium alloy metals through certain pressure processing, and are also called titanium processed materials. Most of the titanium processing is through pressure processing, which causes the processed titanium (blank, ingot, etc.) to produce plastic deformation. According to the different processing temperatures of titanium materials, it can be divided into two types: cold processing and hot processing. According to the processing technology and product formation, it can be roughly divided into several categories such as plates, bars, pipes, forgings, castings, and so on. Widely used in high-end fields, such as high-end chemical, aerospace, medicine, and marine engineering, the demand for titanium processing materials in high-end fields has increased significantly, especially in the aerospace field.
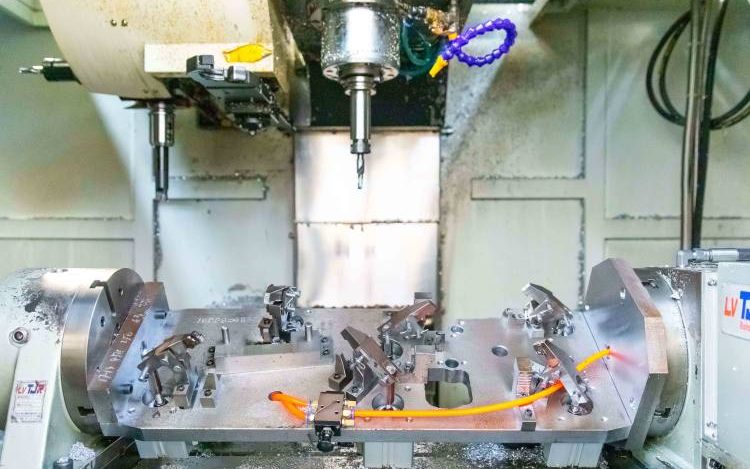
CNC Machining Titanium Materials
Titanium ores are mainly ilmenite and rutile. The two most prominent advantages of titanium are high specific strength and strong corrosion-resistance, which determines that titanium must have broad application prospects in aerospace, weaponry, energy, chemical industry, metallurgy, construction, and transportation. The abundant reserves provide a resource base for the wide application of titanium.
| Yield Strength | Elongation at Break | Hardness | Density | Max Temp |
| 120,000 PSI | 10% | Rockwell C30 | 0.16 lbs / cu. in | 3000°F |
CNC Machining Titanium Material Properties
Low density: the density of metal titanium is 4.51g/cm3, which is about 50% of copper and 77% of low carbon steel.
Corrosion resistance: It can generate an oxide film from titanium in the air. And it is almost completely noncorrosive by seawater. Known as “marine metal” corrosion. Chlor-alkali, soda ash, vacuum salt production, petrochemicals, ships, desalination, nuclear power plants, thermal power desulfurization, etc.
Temperature performance: The new titanium alloy can be used temporarily at 600°C or higher, and maintains ductility and toughness especially suitable for space coke consumption at low temperatures of -196~-253°C. Therefore, it is called “space metal”, aerospace, refrigeration industry, and other biocompatibility without metal allergy. Known as the “biometal” key information.
Superconductivity: The wire made of niobium-titanium alloy exhibiting zero resistance below the critical temperature can pass through any power equipment and other superconducting properties. At present, the consumption of titanium materials in my country is mainly in the fields of the chemical industry, aerospace and sports, and leisure.

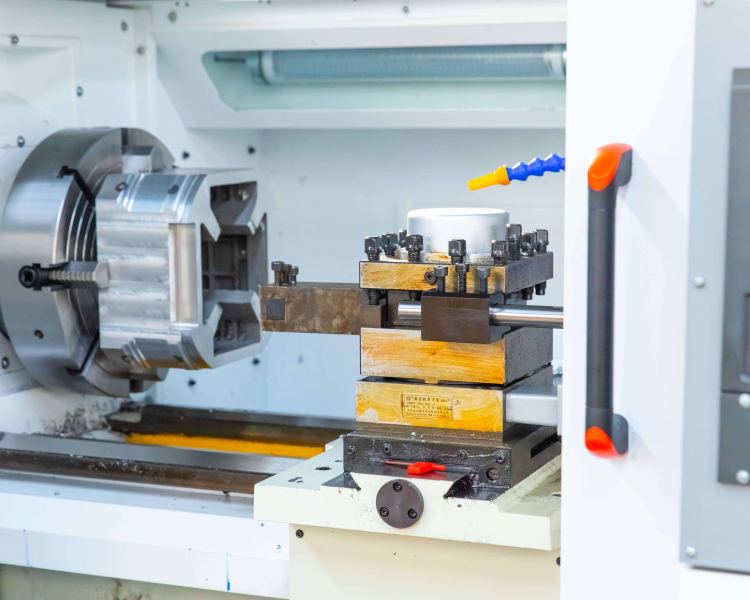
CNC Machining for Titanium – The Most Powerful Titanium Parts Manufacturer
As all know, Titanium is a material that is hard to be machined, to support a perfect titanium part, a manufacturer needs to be equipped with professional machines and an experienced CNC machining tech team. JTR is one of the most powerful Titanium parts manufacturers, who has stuck in CNC parts production, we are able to give our customers some professional engineering support and support them at a competitive price, and our produced parts will all be in high precision.
Advantage of Our CNC Machining Titanium Service
- Machining center can process multiple at the same time to improve production efficiency.
- It can improve the machining accuracy of parts and the product consistency is good. The machining center has a compensation function to obtain the machining accuracy of the machine tool itself.
- Has a wide range of adaptability and greater processing flexibility.
- It can realize multiple functions in one machine. The machining center can perform a series of processing such as milling, drilling, boring, tapping, etc.
- Accurate cost and expenditure can be carried out, and the production cycle can be shortened.
- There is no need for special fixtures, which can save costs and shorten the production cycle.
- It can supply props with sufficient hardness to perfectly meet the design needs of customers.

CNC Machining Titanium FAQs