If you’re considering 3D printing, the first technical question is simple — SLA or FDM? But the answer depends on what you actually need: visual appeal, mechanical strength, cost control, or a mix of all three. This guide breaks down the real, practical differences between SLA and FDM 3D printing, helping you make an informed, no-regret decision.
What Exactly Are SLA and FDM 3D Printing?
What is FDM 3D Printing?

FDM 3D printing (Fused Deposition Modeling) is the most common type of 3D printing, especially for beginners and practical users.
| How It Works | Heated plastic filament is extruded through a nozzle, building the object layer by layer — imagine a precise, motorized glue gun. |
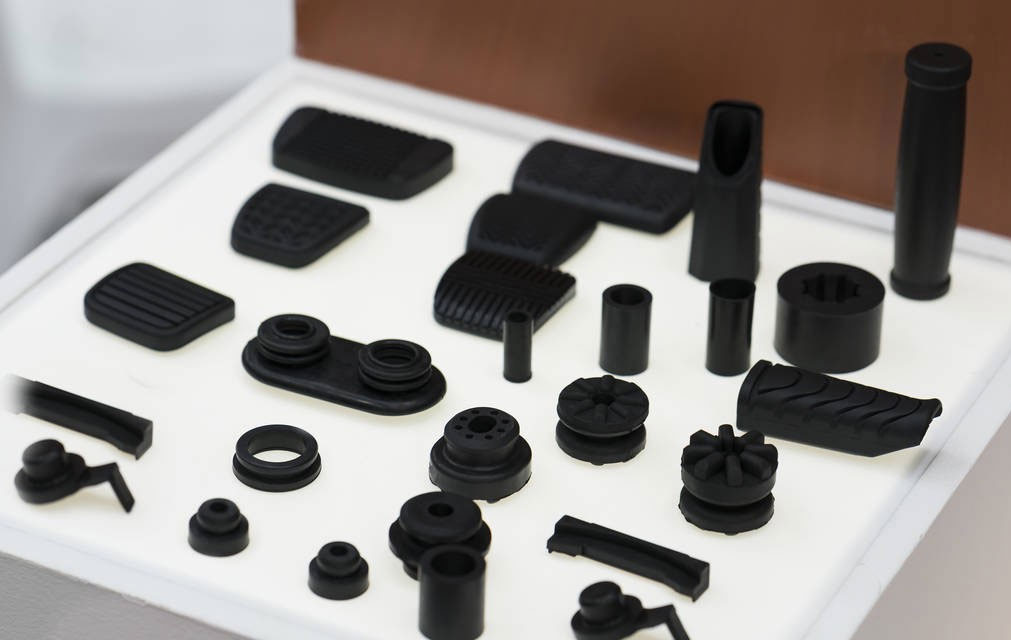
| Pros of FDM | ✅ Affordable printers and materials ✅ Easy to use and widely accessible ✅ Works with various plastics like PLA, ABS, TPU ✅ Good for functional parts, prototypes, hobby projects |
| Cons of FDM | ⚠ Visible layer lines, rougher surfaces ⚠ Lower resolution compared to resin printing ⚠ Some complex shapes require support structures ⚠ Limited fine detail for intricate models |
| FDM is suitable for | Affordable prototyping Mechanical parts or brackets Educational use and maker projects |
What is SLA 3D Printing?

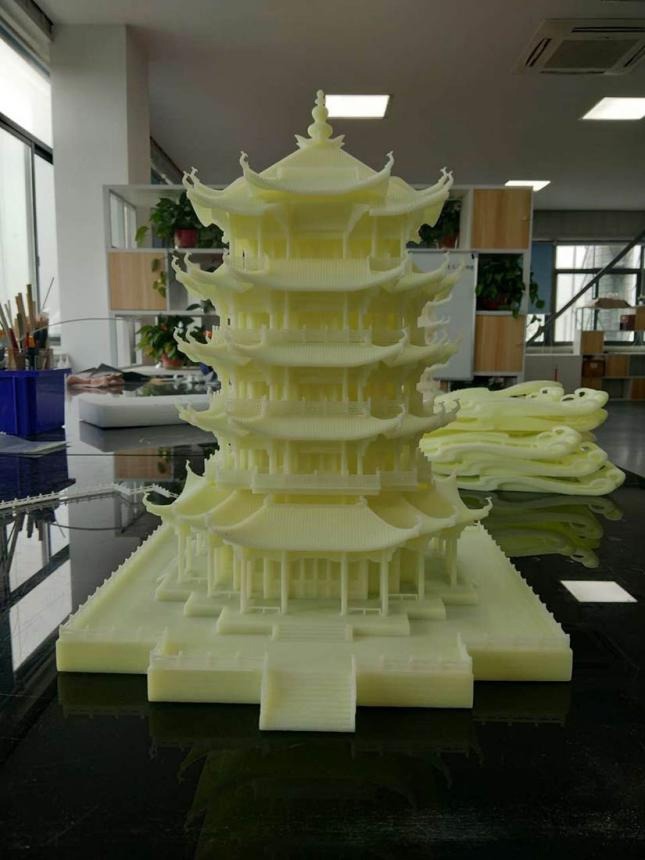
SLA 3D printing (Stereolithography) is a resin-based 3D printing technology used for high-detail, smooth-surface parts.
| How It Works | A UV laser selectively cures liquid resin, hardening one layer at a time with extreme precision. |
| Pros of FDM | ✅ Superior surface finish, minimal layer lines ✅ High-resolution, sharp details ✅ Perfect for small, intricate, or cosmetic parts ✅ Wide range of specialty resins for different functions |
| Cons of FDM | ⚠ More expensive materials and equipment ⚠ Resin handling requires care (chemical exposure) ⚠ Additional post-processing: washing, UV curing ⚠ Some resin parts can be brittle without special formulations |
| SLA is suitable for | Detailed prototypes for presentation Dental models, jewelry, artistic pieces Small, complex components requiring high precision |
What are the Differences Between SLA 3D Printing and FDM 3D Printing?
Understanding the real technical and practical differences helps you avoid costly mistakes. Let’s compare:
| Feature | FDM 3D Printing | SLA 3D Printing |
| Process | Melted plastic extruded through nozzle | UV laser cures liquid resin layer by layer |
| Precision | Moderate (~±0.5 mm), visible layer lines | High (~±0.05 mm), smooth finish, sharp details |
| Surface Finish | Rougher, visible lines, may require sanding | Smooth, minimal post-processing needed |
| Materials | PLA, ABS, TPU, Nylon, blends (plastic spools) | Photosensitive resins (rigid, flexible, castable) |
| Strength | Durable with tough plastics (e.g., ABS) | Detailed but may be brittle unless engineered resin used |
| Costs | Lower printer and material prices, accessible | Higher upfront and resin costs, more maintenance |
| Post-Processing | Simple trimming, sanding if needed | Cleaning with alcohol, UV curing required |
| Best For | Prototypes, brackets, practical parts | Show-quality models, intricate designs |
SLA and FDM–Which Should You Choose?
Choosing between SLA and FDM isn’t about “better or worse” — it’s about what suits your actual project needs:
| Project Type | Recommended Technology |
| Fast, affordable functional prototypes | FDM |
| Large structural parts for testing | FDM |
| High-detail visual prototypes | SLA |
| Jewelry master models or dental parts | SLA |
| Flexible parts like seals or grips | FDM with TPU |
| Artistic or display-quality miniatures | SLA |
Simple Decision Guide:
✅ On a budget? Prioritize function? → FDM
✅ Need fine detail, smooth surface, cosmetic quality? → SLA
✅ Unsure? Many professional services offer both — test your design with each method before investing.
Final
- FDM brings affordability, practicality, and accessibility.
- SLA offers high detail, surface quality, and professional finish.
No single method fits every situation. By understanding both, you can confidently choose based on real-world needs — avoiding wasted time, money, and frustration.
Pro Tip: Combine both in one project — use FDM for structural parts, SLA for detailed components — balancing cost and performance.