There are a variety of materials that can be applied to 3D printing, and 3D printing allows manufacturers to freely choose the size, texture and strength of the product. The variety of materials that can be used expands as the market value for 3D printing does. Although PLA is currently the primary material used for 3D printing at home, raw elements including metal, graphite, and carbon fiber are also frequently used. Let’s know these materials in details.

What is The Most Frequently Used Material in 3D Printing?
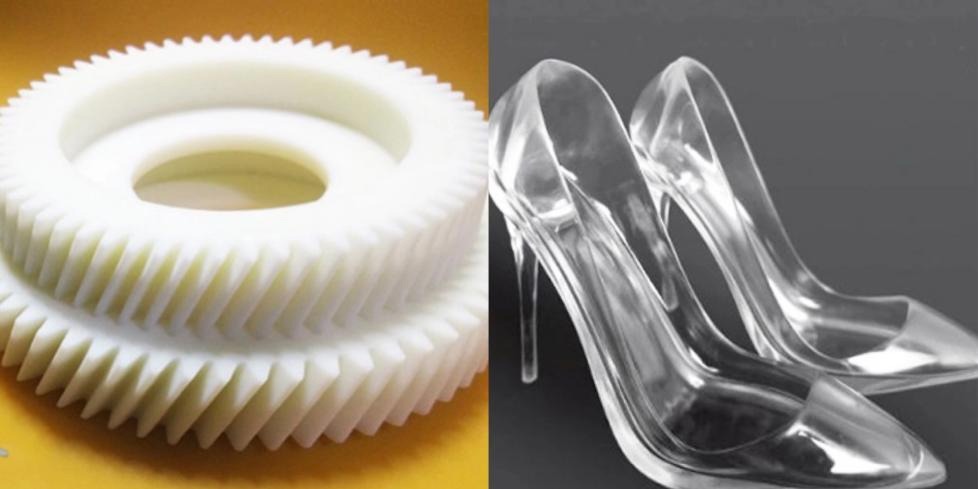
The most popular raw material for 3D printing right now is plastic.
Plastic has several advantages over other raw materials for 3D printing, including strength, flexibility, smoothness, and color availability. Plastics are also frequently affordable, which makes them perfect for both producers and consumers.
In 3D printing, two types of plastic are most frequently employed:
- PLA: The most well-liked 3D printing substance is polylactic acid (PLA). This biodegradable plastic is created from renewable resources like cornstarch. It is simple to use at home thanks to its low melting point.
- ABS: Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) is ideal for parts that need to be strong and flexible, such as those found in automobiles or home appliances. It’s also renowned for being inexpensive.
Additional Materials Used in 3D Printers
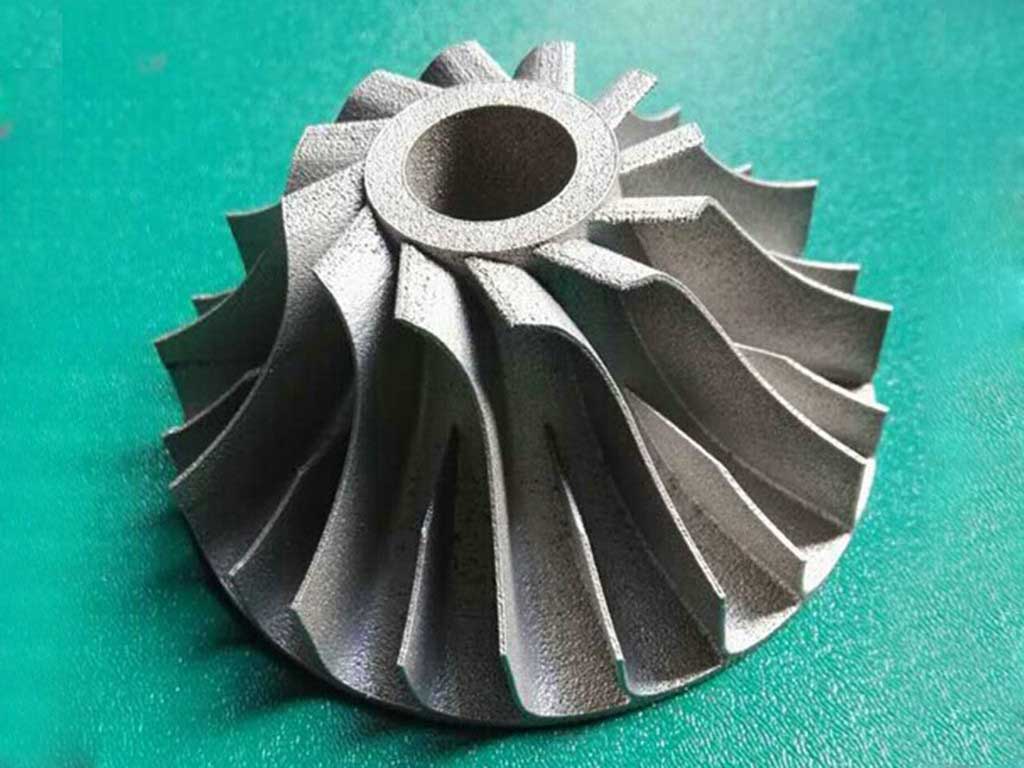
- Metal
Metal is used for ready-to-install components, completed goods, and prototypes. The process is known as direct metal laser sintering (DMLS), and it may be used to create both prototypes and final industrial products. DMLS printing has been used by the aviation sector to produce ready-to-install parts and streamline operations since it was first introduced.
- Graphene and graphite
Graphene and graphite are often used for lighting and electronics. Compared to other conductors now on the market, graphene conducts electricity more efficiently and is stronger, lighter, and easier to insulate.

- Carbon fiber
Carbon fiber is utilized for electrical wire installation, components, and bearings. Similar to graphite, carbon fiber can be combined with more common plastics to produce composite materials that can be as strong as steel while using less intensive than aluminum.
- Powder
The powder is melted and distributed in layers during 3D printing, giving the finished product the correct thickness, texture, and pattern.
Typical varieties of powder include:
- Nylon: Polyamide can produce fine features on 3D printed objects because to its good flexibility and durability.
- Aluminide: A mixture of polyamide and gray aluminum, aluminide powder is used to create some of the strongest 3D printed sculptures. This powder, which is recognizable by its granular and sandy appearance, can be utilized to create industrial prototypes.
- Resins
Resins have more constraints than other materials, generally speaking. Resins are less flexible and strong than other 3D printing-friendly materials. The most common resin colors are clear, black, and white, but some prints are also available in orange, red, blue, and green.
It is primarily utilized in SLA, DLP, Multijet, and CLIP technologies. Castable resins, tough resins, flexible resins, and other forms of resin can all be utilized in 3D printing.
Unique features of resins:
- Photopolymerization: Unlike filaments that melt and solidify, resins are photopolymers. This means they exist as liquids and cure into solid forms when exposed to light, typically ultraviolet (UV) light. This allows for incredibly precise solidification at the microscopic level, leading to high resolution prints.
- Wide Range of Mechanical Properties: While offering diverse options like filaments, resins boast a broader spectrum of mechanical properties:
Flexibility: Unlike most filament options, resins can achieve rubber-like properties, making them suitable for applications like gaskets, seals, and flexible components.
Biocompatibility: Certain resins are specially formulated to be biocompatible, meaning they are safe for use in the human body. This opens doors for applications like surgical guides, dental models, and even custom implants.
Castability: Some resins are castable, meaning they can be used to create intricate jewelry designs or dental applications through a process where the resin is burned out cleanly, leaving a mold for other materials.
- Translucency and Coloration: Resins offer a wider range of translucent and opaque options compared to most filaments. This allows for the creation of parts that mimic the appearance of glass or other translucent materials. Additionally, resins can be readily dyed or pigmented to achieve a wider variety of colors compared to the limited color options typically available in filaments.
- Isotropic Properties: Unlike many filaments that exhibit different mechanical properties depending on the printing direction due to the layering process, resins typically display isotropic properties. This means their strength and other characteristics are consistent in all directions, making them ideal for applications requiring uniform performance.
- Ceramics
One of the newest materials utilized in 3D printing is ceramic. Since it can take severe heat and pressure without even breaking or warping, it is more durable than metal and plastic. Additionally, unlike other metals and polymers, this sort of material does not wear away or become corroded easily.
It boasts high-precision parts with a smooth, shiny surface as its distinguishing features. Additionally, it is resistant to lye, heat, and acid. It comes in a variety of colors.
Disadvantages of ceramic in 3D printing:
For ceramic to melt, a high temperature is needed.
For glazing and kilning procedures, it is not suited.
It is limited in its ability to print items with enclosed and interlocking elements because of its fragility.
For piece assembly, it is not ideal.

Conclusion
If you want to enjoy the ease of 3D printing, you can just outsource to a reliable 3D printing service provider. Your company doesn’t need to do 3D design and printing, mechanical design and drafting, 3D design modelling services and in-house as they all can be done professionally with quality and accuracy by JTR.