CNC machining is at the heart of modern manufacturing, but not all CNC machines are created equal. If you’ve been researching CNC solutions, you’ve probably come across terms like 3-axis, 4-axis, and 5-axis machining—but what do they mean? And more importantly, how do you choose the right one for your parts or projects?
What Do 3-Axis, 4-Axis, and 5-Axis Mean?
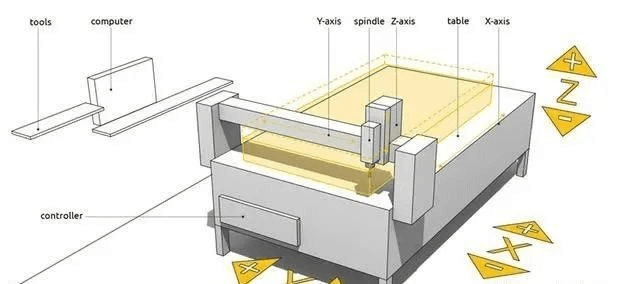
| CNC Type | Axis Explanation | Movement Capability |
| 3-Axis | X (left-right), Y (front-back), Z (up-down) | Tool moves in straight lines; workpiece remains fixed |
| 4-Axis | 3 linear + 1 rotational (A-axis or B-axis) | Allows rotation around one axis—ideal for multi-side parts |
| 5-Axis | 3 linear + 2 rotational (A/B + B/C) | Simultaneous rotation and translation for full 3D geometry |
What are the Differences between 3-axis, 4-axis, and 5-axis CNC machining?
Key Differences between 3-axis, 4-axis, and 5-axis CNC machining?
| Feature | 3-Axis | 4-Axis | 5-Axis |
| Motion | X, Y, Z | X, Y, Z + A | X, Y, Z + A + B/C |
| Setup Complexity | Simple | Moderate | Advanced |
| Workpiece Rotation | None | One direction | Two directions (simultaneous) |
| Geometric Capability | Flat & 2.5D parts | Side features, basic contours | Complex contours, cavities, and undercuts |
| Typical Use Cases | Plates, brackets | Shafts, cams, side features | High upfront and maintenance costs Skilled labor and sophisticated CAM software required |
| Pros | Most affordable Fast and simple to operate Ideal for basic parts and small batches | Enables machining on multiple sides in one setup Increases productivity and consistency Supports circular or rotational features | Access to all surfaces in one setup Highest accuracy, surface finish, and efficiency Essential for complex, high-tolerance parts |
| Cons | Requires manual repositioning for multi-face machining Limited support for 3D shapes and complex surfaces | Not capable of full 5-sided machining Requires intermediate programming skills | High upfront and maintenance costs Skilled labor and sophisticated CAM software are required |
Industry Use Cases & Applications: Differences between 3-axis, 4-axis, and 5-axis
| CNC Type | Typical Industries | Part Examples |
| 3-Axis | Consumer electronics, general machining | Plates, brackets, fixtures |
| 4-Axis | Automotive, robotics, machine tools | Shafts, gears, turbine housings |
| 5-Axis | Aerospace, medical, mold manufacturing | Blisks, orthopedic implants, injection molds |
Machine Investment & ROI Considerations:Differences between 3-axis, 4-axis, and 5-axis
| Factor | 3-Axis | 4-Axis | 5-Axis |
| Typical Cost | $20K–$60K | $50K–$120K | $150K–$500K+ |
| Setup Time | High | Moderate | Low |
| Cycle Time Efficiency | Basic tasks only | Reduced handling time | Highest throughput |
| ROI Cycle | Short for prototyping | Moderate for small-to-mid production | Long-term, high-margin parts |
Capability Limitations:Key Differences between 3-axis, 4-axis, and 5-axis CNC machining?
| Limitation Type | 3-Axis | 4-Axis | 5-Axis |
| Undercuts/Hidden Surfaces | ❌ Unsupported | ❌ Limited | ✅ Fully Supported |
| Tool Accessibility | Limited | Moderate | High |
| Multi-Surface Accuracy | Manual re-fixture needed | Improved | Best-in-class |
Programming & Talent Requirements:Differences between 3-axis, 4-axis, and 5-axis CNC machining?
| CNC Level | Programming Skill Level | CAM Software Required | Talent Pool Availability |
| 3-Axis | Entry level | Fusion 360, Mach3 | Broad and accessible |
| 4-Axis | Intermediate | Mastercam, SolidCAM | Growing demand |
| 5-Axis | Expert | Siemens NX, PowerMill | Niche, higher salary required |
Conclusion
| ✅ Choose 3-Axis If: | ✅ Choose 4-Axis If: | ✅ Choose 5-Axis If |
| Your parts are flat, simple, and low-cost You’re prototyping or in early-stage manufacturing | You need better efficiency Your designs involve shafts, profiles, or multi-face workpieces | Precision, geometry complexity, or surface finish is mission-critical You’re working in aerospace, medical, or high-end mold sectors |