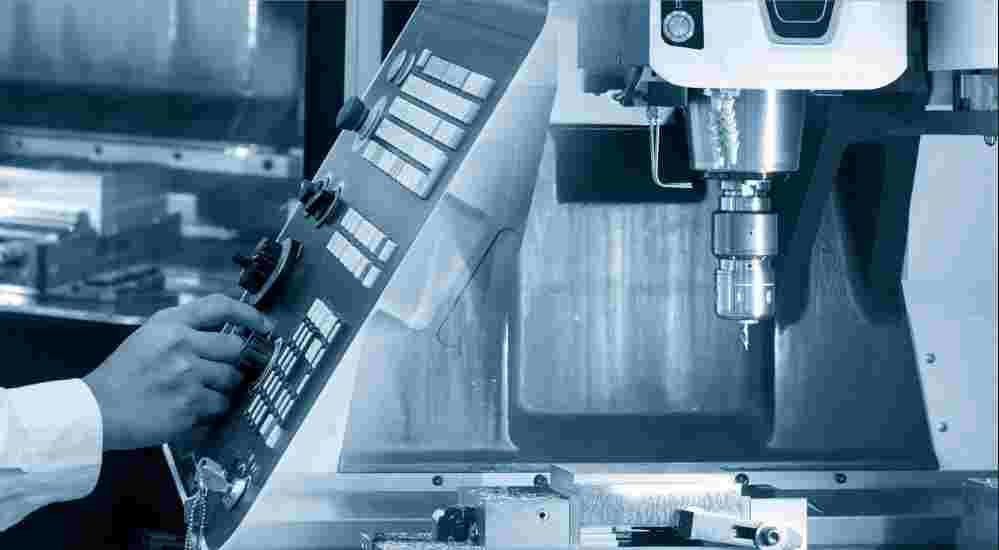
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining is a popular manufacturing method used to produce high-precision parts for a wide range of applications. CNC machines use pre-programmed computer software to control the movement of cutting tools and other machining tools, allowing for precise and repeatable production of complex parts. One important distinction in CNC machining is the number of axes or directions that the cutting tool can move, which affects the types of geometries that can be produced and the level of precision and accuracy that can be achieved.
In this article, we’ll explore the difference between 3-axis and 5-axis CNC machining. We’ll start by defining each method and explaining how they work, then compare their advantages and limitations. Whether you’re a manufacturing engineer, a product designer, or a hobbyist looking to improve your CNC machining skills, understanding the difference between 3-axis and 5-axis machining is essential for choosing the right method for your project.

1. What is 3-axis CNC machining?
3-axis CNC machining is a popular method of production that uses pre-programmed software to control the movement of cutting tools in three directions: X, Y, and Z. While 3-axis machining is not as versatile as 5-axis machining, it has its own set of advantages and limitations.
Advantages of 3-axis CNC machining:
- Lower cost: 3-axis machines are typically less expensive than 5-axis machines, making them a more affordable option for small businesses and hobbyists.
- Simpler programming: 3-axis machining is generally easier to program and set up than 5-axis machining, making it a more accessible option for those new to CNC machining.
- Efficient for simple geometries: 3-axis machining is efficient and effective for parts with simple geometries, such as flat or slightly curved surfaces.
- Wide range of materials: 3-axis machines can work with a wide range of materials, including metals, plastics, and composites.
Limitations of 3-axis CNC machining:
- Limited flexibility: 3-axis machines are limited to cutting in three directions, which can make it difficult to machine complex geometries and undercuts.
- Limited precision: 3-axis machines may have limitations in achieving high precision and accuracy for parts with tight tolerances or complex geometries.
- Longer production time: 3-axis machines may require multiple setups to produce complex parts, which can lead to longer production times.
- Limited surface finish: 3-axis machines may produce a rougher surface finish than 5-axis machines, requiring additional post-processing steps.
Overall, 3-axis CNC machining is a reliable and cost-effective option for parts with simple geometries and lower precision requirements. While it has some limitations, it remains a popular choice for many applications and industries. Here are some examples of parts that can be produced using 3-axis machining:
Examples of parts produced using 3-axis machining
- Flat parts: 3-axis machining is ideal for producing flat parts, such as brackets, plates, and frames, which require cutting in only two dimensions.
- Enclosures: 3-axis machining is commonly used for producing enclosures for electronic devices, such as computer cases, phones, and tablets.
- Mold cavities: Mold cavities for injection molding or casting can be produced using 3-axis machining, although more complex molds may require 5-axis machining.
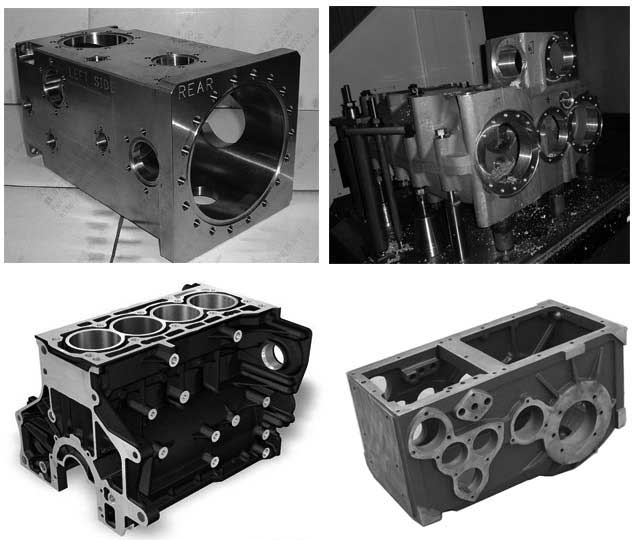
- Automotive parts: 3-axis machining is widely used in the automotive industry to produce parts such as engine blocks, transmission cases, and suspension components.
- Aerospace parts: Parts for the aerospace industry, such as wing ribs, brackets, and engine components, can be produced using 3-axis machining.
- Medical components: 3-axis machining can be used to produce medical components such as prosthetic limbs, dental implants, and surgical instruments.
In conclusion, 3-axis machining is a versatile and cost-effective method for producing parts with simple geometries and lower precision requirements. However, for more complex parts with tight tolerances or undercuts, 5-axis machining may be necessary.
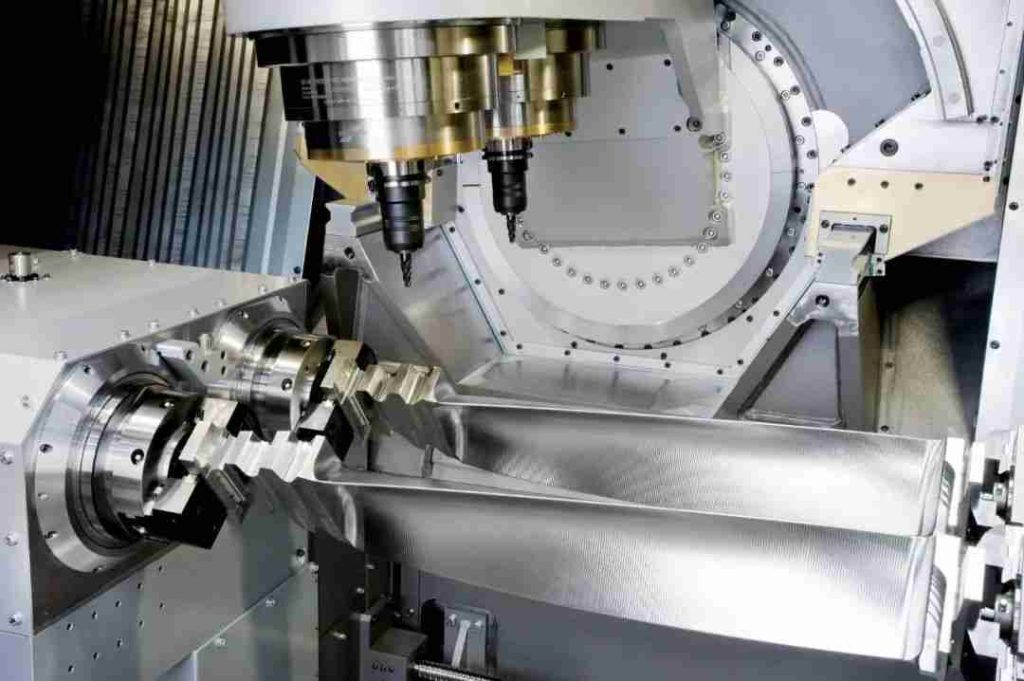

2. What is 5-axis CNC machining?
5-axis CNC machining is a high-precision manufacturing method that can produce complex parts with great accuracy and efficiency. In this section, we’ll explore the advantages and limitations of 5-axis CNC machining.
Advantages of 5-axis CNC machining:
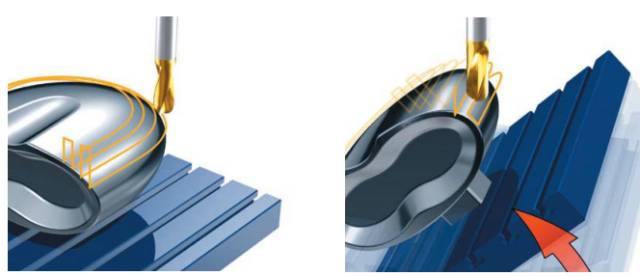
- Greater flexibility: 5-axis machining can move the cutting tool in five directions, which allows for more flexibility in machining complex geometries and undercuts.
- Higher precision: 5-axis machines can achieve higher precision and accuracy in parts with tight tolerances or complex geometries, reducing the need for additional post-processing steps.
- Faster production time: 5-axis machines can produce parts in a single setup, reducing the number of setups required and resulting in faster production times.
- Improved surface finish: 5-axis machining can produce a smoother surface finish on parts, reducing the need for additional post-processing steps.
Limitations of 5-axis CNC machining:
- Higher cost: 5-axis machines are typically more expensive than 3-axis machines, making them less accessible for small businesses and hobbyists.
- Complex programming: 5-axis machining requires more complex programming and setup than 3-axis machining, which can be challenging for those new to CNC machining.
- Limited to smaller parts: 5-axis machines may be limited in the size of parts they can produce, due to the range of motion of the machine and the size of the cutting tools.
- Limited materials: Some materials, such as composites and ceramics, may be difficult to machine with 5-axis machines due to their hardness and brittleness.
Overall, 5-axis CNC machining is a powerful and versatile manufacturing method that can produce complex and high-precision parts with improved surface finish and faster production times. However, it may be more costly and complex than 3-axis machining, and it may have limitations in terms of part size and material compatibility. Here are some examples of parts that can be produced using 5-axis machining:
Examples of parts produced using 5-axis machining
- Aerospace components: 5-axis machining is widely used in the aerospace industry to produce parts such as turbine blades, engine components, and wing ribs. These parts require complex geometries and tight tolerances, which 5-axis machining can achieve with great accuracy.
- Medical implants: 5-axis machining is commonly used to produce medical implants, such as hip and knee replacements, that require complex geometries and high precision. The use of 5-axis machining can result in improved accuracy and faster production times.
- Mold tooling: Mold tooling for injection molding or casting can be produced using 5-axis machining, which allows for the production of complex and precise mold cavities and cores.
- Automotive components: 5-axis machining is used in the automotive industry to produce parts such as engine blocks, transmission cases, and suspension components. These parts require complex geometries and tight tolerances, which 5-axis machining can achieve with great accuracy.
- Sculptures: 5-axis machining can be used to produce sculptures and other works of art with intricate and complex shapes. The use of 5-axis machining can allow artists to create more complex and detailed pieces with greater efficiency and precision.
In conclusion, 5-axis machining is a versatile and powerful method for producing complex and high-precision parts across a range of industries, including aerospace, medical, automotive, and art.
3. How to choose 3-axis and 5-axis CNC machining?
Choosing between 3-axis and 5-axis CNC machining depends on several factors, such as the complexity of the parts, required precision, production volume, available budget, and the materials being used. Here are some considerations to help you decide which machining method is best suited for your needs:
Part complexity: If your parts have simple geometries that can be produced using 3-axis machining, then this may be the most cost-effective option. However, if your parts have complex shapes, undercuts, or multi-sided features, then 5-axis machining may be necessary to achieve the required precision and accuracy.
Required precision: If your parts require high precision and tight tolerances, 5-axis machining may be the best option, as it can achieve greater accuracy and reduce the need for additional post-processing steps.
Production volume: For high-volume production runs, 3-axis machining may be the most cost-effective option, as it typically has faster cycle times and lower operating costs. However, for low-volume or custom production runs, 5-axis machining may be necessary to achieve the required precision and complexity.
Available budget: 5-axis machines are typically more expensive than 3-axis machines, so your available budget may play a role in your decision. If your budget is limited, 3-axis machining may be the more cost-effective option.
Material properties: Some materials, such as composites and ceramics, may require 5-axis machining due to their hardness and brittleness. If you are working with such materials, 5-axis machining may be necessary to achieve the required precision and accuracy.
4. Summary
To draw a conclusion, the choice between 3-axis and 5-axis CNC machining depends on the complexity of the parts, required precision, production volume, available budget, and the materials being used. Consider these factors carefully when making your decision, and consult with a CNC machining expert if you need further guidance.