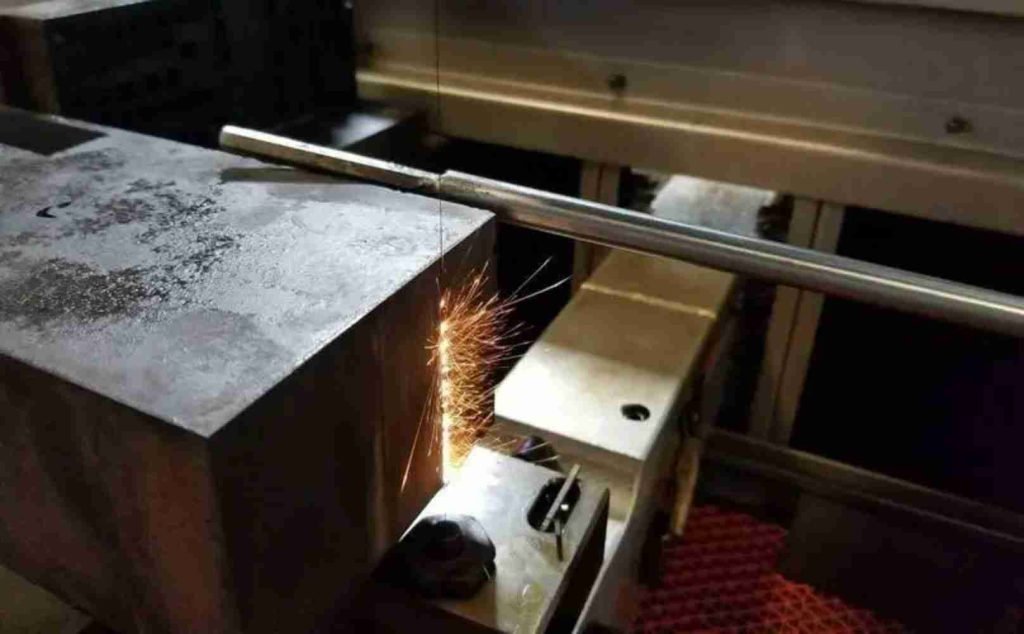
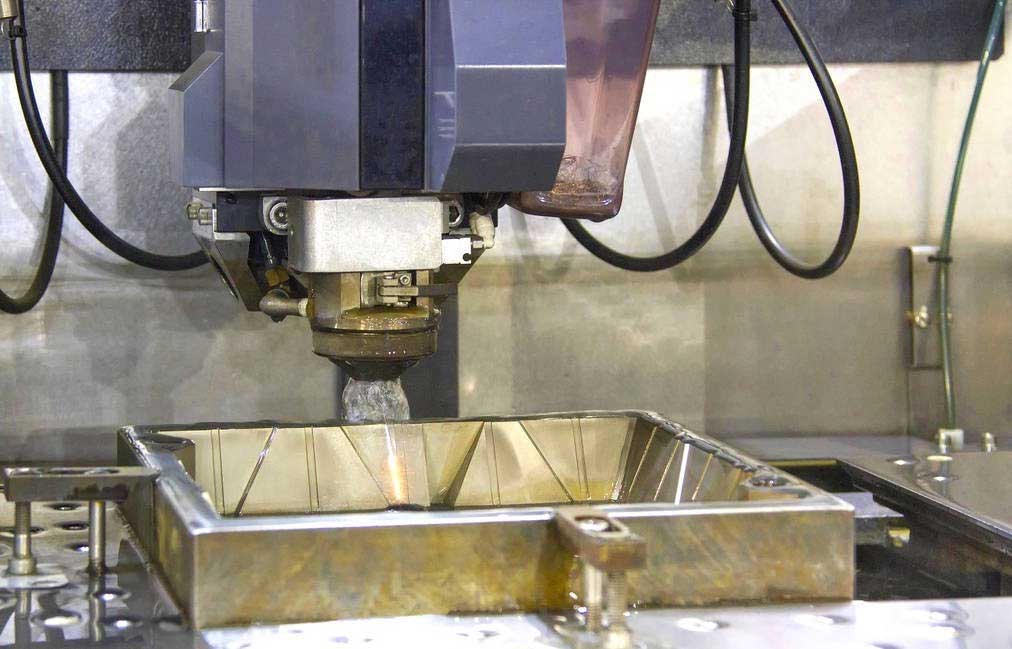
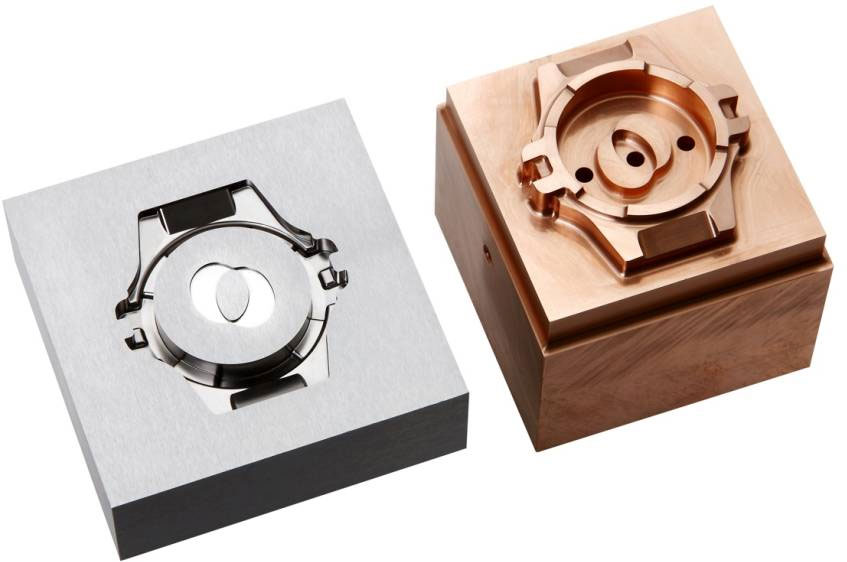
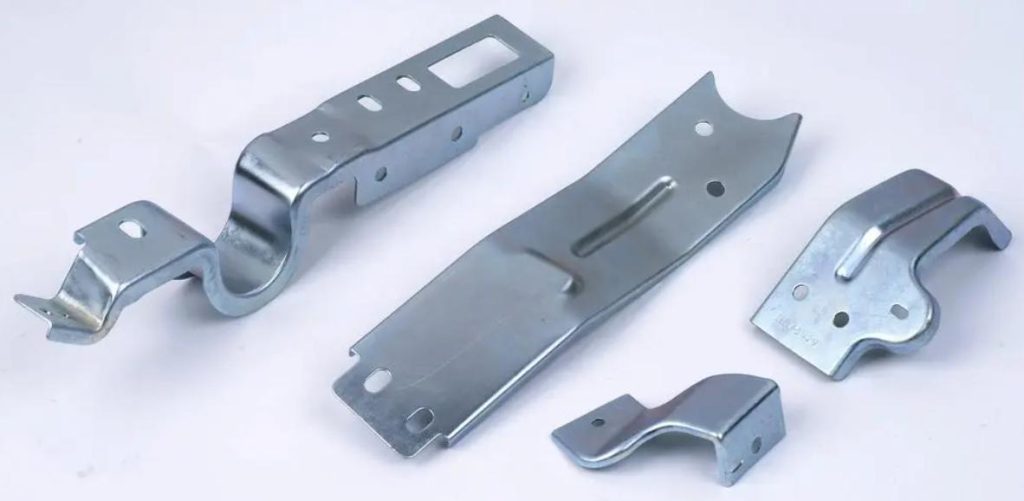
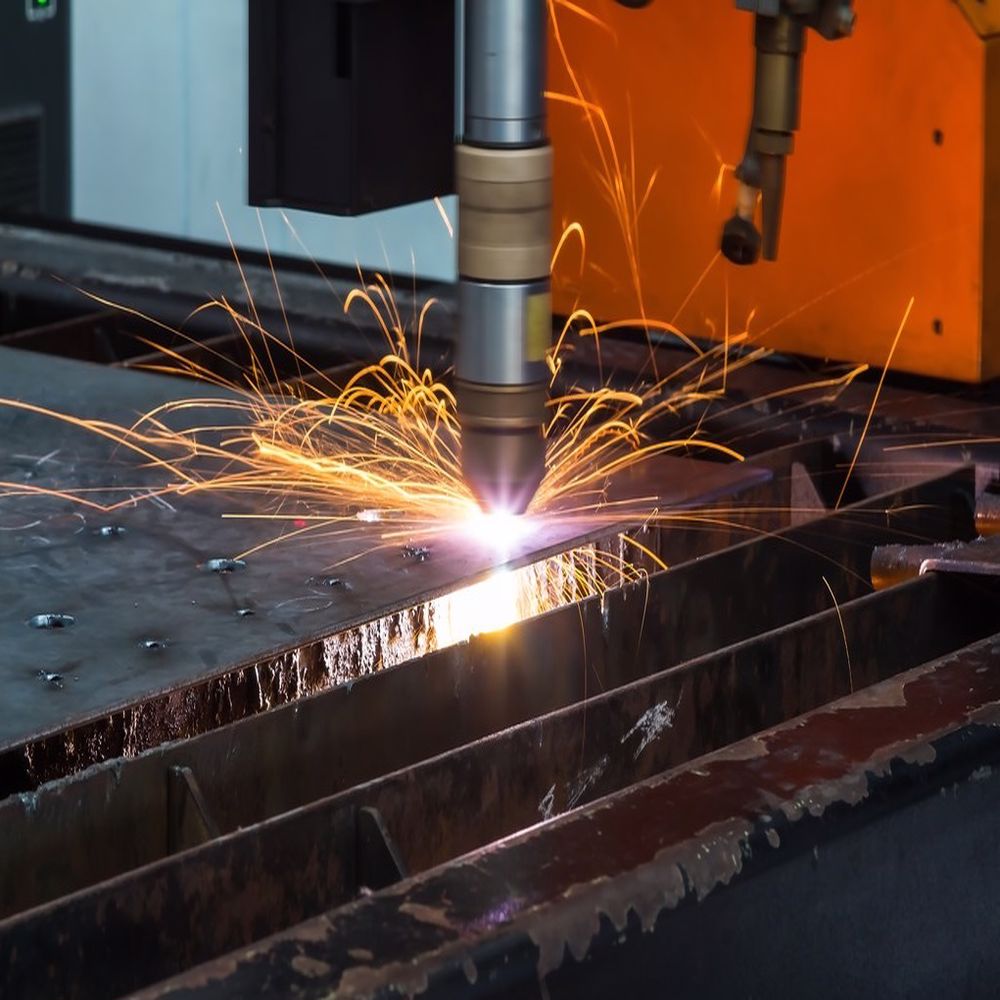
Wire electrical discharge machining (Wire EDM) is a non-traditional machining process that uses a thin wire electrode to cut intricate and complex shapes into conductive materials. It is a highly versatile and precise process, making it ideal for machining stainless steel, a material known for its strength, corrosion resistance, and aesthetic appeal. Here we will talk about common stainless steel types for Wire EDM, their different applications, and some processing tips in Wire EDM.
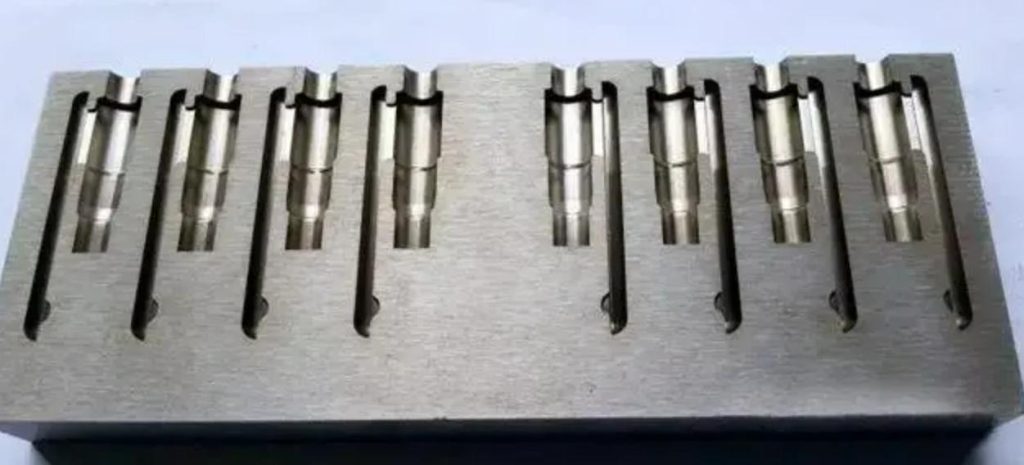

What types of stainless steel can be cut with wire EDM?
There are several types of stainless steel suitable for wire EDM, each offering unique properties and benefits. Here are some of the most commonly used:
- Austenitic stainless steels: These are the most common type of stainless steel, known for their excellent corrosion resistance and formability. Popular grades for wire EDM are:
- 304: The most widely used stainless steel. It is highly formable and weldable, making it ideal for a wide range of applications.
- 316: A more corrosion-resistant version of 304. It is often used in marine and chemical processing applications.
- 303: A free-machining grade of stainless steel. It is easier to machine than other grades, but it is not as strong or corrosion-resistant.
- Martensitic stainless steels: These steels are stronger and harder than austenitic grades, but are less corrosion resistant. They are often used for applications requiring high wear resistance. Popular grades for wire EDM include:
- 410: A low-carbon martensitic stainless steel. It is strong and wear-resistant, but it is not as corrosion-resistant as austenitic grades.
- 420: A high-carbon martensitic stainless steel. It is even stronger and harder than 410, but it is also less corrosion-resistant.
- Precipitation-hardening stainless steels: These steels offer a good balance of strength, corrosion resistance, and machinability. They can be hardened to achieve specific properties. Popular grades for wire EDM include:
- 17-4PH: A precipitation-hardening stainless steel with excellent strength and corrosion resistance. It is often used in aerospace and medical applications.
The choice of stainless steel for wire EDM depends on the specific application requirements. Factors such as desired strength, corrosion resistance, and machinability must be considered.
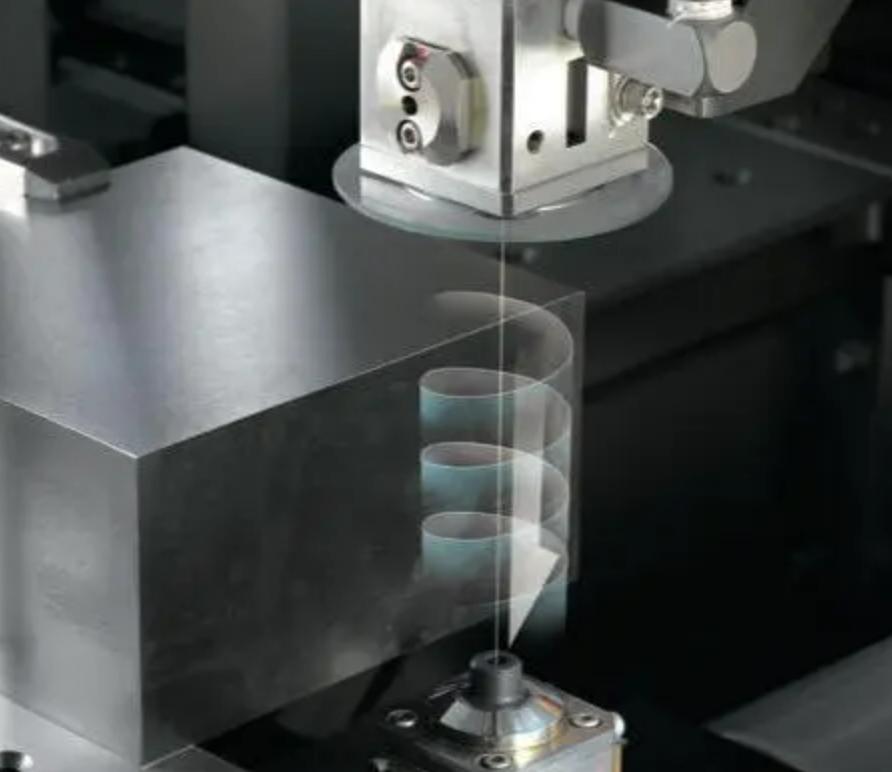

What are the common applications for wire EDM stainless steel?
Wire EDM stainless steel has a wide range of applications due to its versatility, precision, and ability to cut complex shapes. Here are some of the most common applications:
- Aerospace:
- Turbine blades: Wire EDM is used to create the intricate shapes required for turbine blades.
- Engine components: Wire EDM is used to create high-precision engine components with tight tolerances.
- Landing gear: Wire EDM is used to create the complex shapes required for landing gear components.
- Medical:
- Surgical instruments: Wire EDM is used to create sharp, precise surgical instruments with smooth surfaces.
- Implants: Wire EDM is used to create custom-designed implants for medical applications.
- Dental tools: Wire EDM is used to create dental tools with sharp edges and smooth surfaces.
- Automotive:
- Fuel injectors: Wire EDM is used to create the precise holes required for fuel injectors.
- Transmission gears: Wire EDM is used to create gears with high precision and smooth surfaces.
- Valve components: Wire EDM is used to create valve components with precise dimensions and smooth surfaces.
- Electronics:
- Circuit boards: Wire EDM is used to create precise circuit board patterns.
- Semiconductor components: Wire EDM is used to create small, complex semiconductor components with high precision.
- Connectors: Wire EDM is used to create connectors with precise dimensions and smooth surfaces.
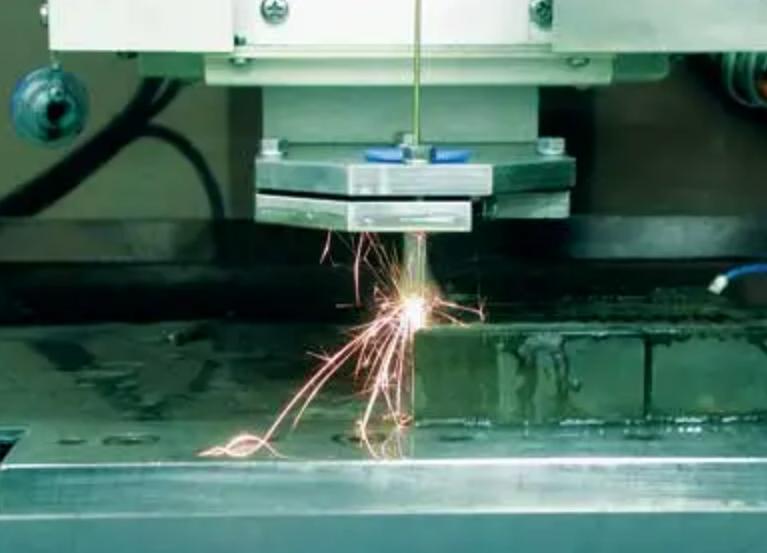

Technical Tips for Wire EDM Stainless Steel
What are the optimal wire EDM settings for different stainless steel grades?
The optimal wire EDM settings for different stainless steel grades vary depending on the specific grade, thickness, and desired outcome. However, some general guidelines can be followed:
- Material:
- Austenitic stainless steels (300 series): These are the most common type of stainless steel and are generally easier to machine than other grades. They often require lower pulse-on times, higher pulse-off times, and lower peak currents to achieve good results.
- Martensitic stainless steels (400 series): These steels are harder and more difficult to machine than austenitic grades. They typically require higher pulse-on times, lower pulse-off times, and higher peak currents.
- Ferritic stainless steels (400 series): These steels are similar to martensitic grades in terms of machinability. They require similar settings to martensitic steels.
- Precipitation-hardening stainless steels (PH series): These steels are the most difficult to machine due to their high strength and hardness. They require very specific settings and careful monitoring to achieve good results.
- Wire diameter:
- Smaller diameter wires are more prone to breakage, so they require lower cutting speeds and feed rates.
- Larger diameter wires can handle higher cutting speeds and feed rates, but they will also wear out the electrode more quickly.
- Desired outcome:
- High cutting speed: Use higher pulse-on times, lower pulse-off times, and higher peak currents.
- Good surface finish: Use lower pulse-on times, higher pulse-off times, and lower peak currents.
- High accuracy: Use slower cutting speeds and feed rates.
Here are some suggested starting points for wire EDM settings for different stainless steel grades:
| Grade | Pulse-on time (µs) | Pulse-off time (µs) | Peak current (A) | Cutting speed (mm/min) |
| 304 | 50 | 50 | 10 | 10 |
| 316 | 60 | 60 | 12 | 8 |
| 410 | 70 | 70 | 14 | 6 |
| 430 | 80 | 80 | 16 | 4 |
| 17-4 PH | 90 | 90 | 18 | 2 |
How can I minimize wire consumption and electrode wear in wire EDM stainless steel?
Minimizing wire consumption and electrode wear in wire EDM stainless steel is crucial for maximizing efficiency and reducing costs. Here are some effective strategies:
- Optimize Cutting Parameters:
- Reduce discharge current: Lower current reduces the size of each spark, resulting in less material removal and less electrode wear.
- Increase pulse duration: Longer pulse durations allow more material to melt and be removed with each spark, reducing the number of sparks needed and extending wire life.
- Increase pulse interval: Longer intervals between pulses allow the electrode to cool, reducing wear.
- Optimize wire feed rate: A faster wire feed rate removes material more quickly, reducing the amount of time the electrode is exposed to the spark and minimizing wear.
- Maintain constant wire tension: Proper tension ensures the wire is straight and stable, reducing the risk of wire breaks and ensuring efficient cutting.
- Use High-Quality Electrode Wire:
- Select the appropriate wire diameter: Thinner wires generally provide better surface finishes but wear faster. Thicker wires are more durable but may leave a rougher finish.
- Choose a wire with a good balance of strength and conductivity: This ensures efficient cutting and minimizes wear.
- Use coated wire: Coatings can improve lubrication and reduce friction, extending wire life.
- Maintain Proper Dielectric Fluid:
- Use clean, filtered dielectric fluid: Contaminants in the dielectric fluid can increase wear and tear on the electrode and workpiece.
- Maintain the correct dielectric fluid level: Insufficient fluid can lead to sparking and increased wear.
- Use deionized water: Deionized water has a higher resistivity than tap water, which reduces sparking and electrode wear.
By following these tips, you can ensure successful and efficient wire EDM of stainless steel components, achieving the desired precision, quality, and performance. If you are looking for a reliable manufacturer of wire EDM services, please feel free to contact JTR.










