Precision CNC Turning and Finishing for Different Industry Components
High-precision construction is necessary to continue developing new medical devices,…
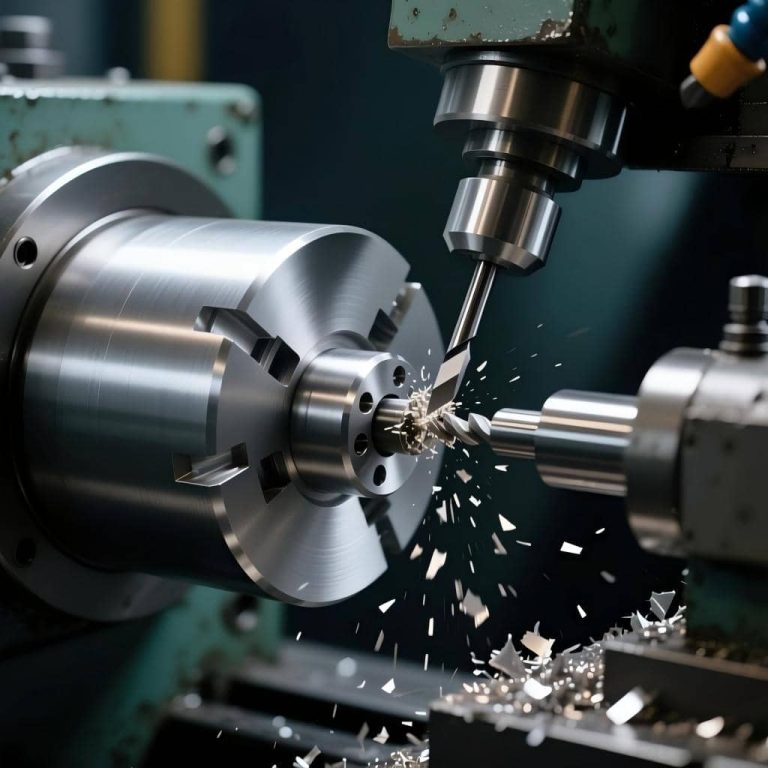


High-precision construction is necessary to continue developing new medical devices,…
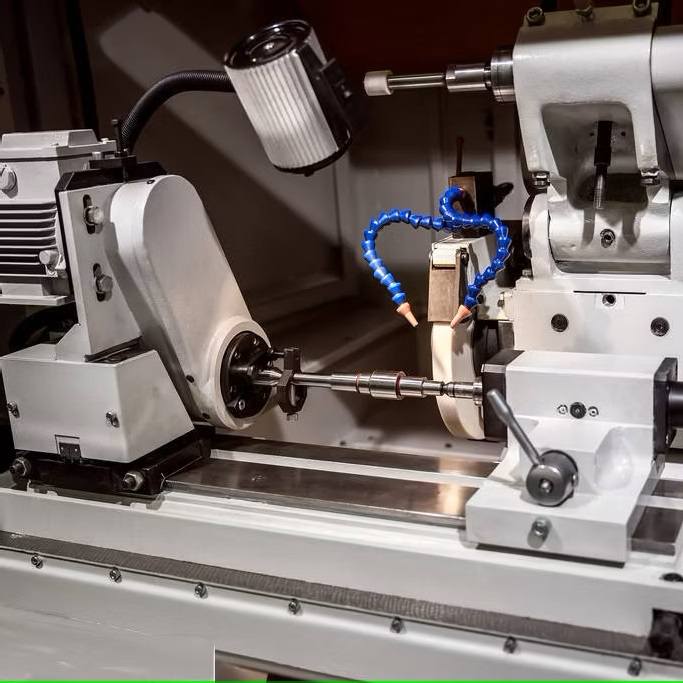
In the last 10 years, many industries around the world…
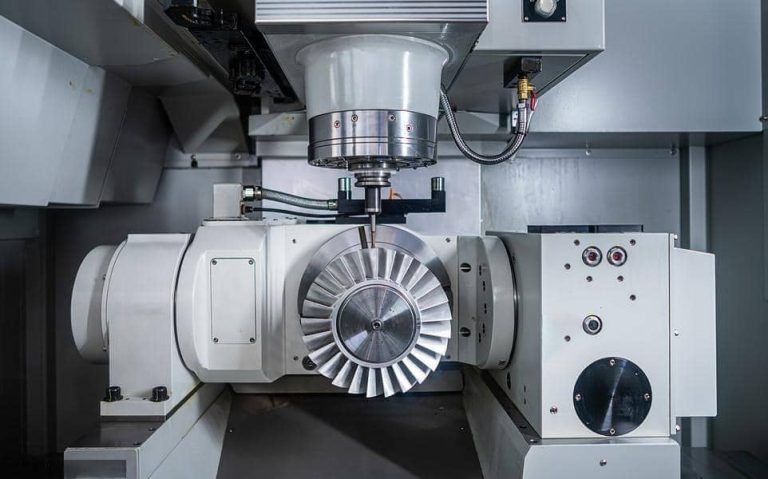

What Is the Hardest Material to CNC Machine?

What Is the Hardest Material to CNC Machine?

The global manufacturing landscape has witnessed a significant shift, with…

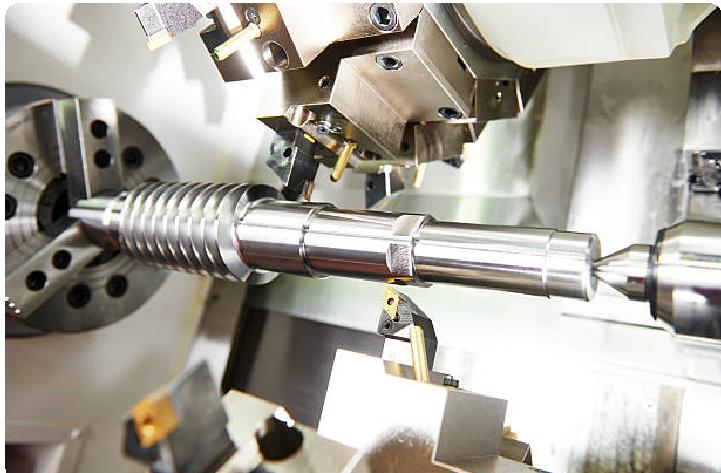
How Precise is CNC Turning?

What You Must Know Before Choosing CNC Machining Services

What is CNC Milling and Turning?

What is CNC Turning?

How to Use G41 and G42 in CNC Turning

CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining is a widely used manufacturing…

Brass, a versatile copper-zinc alloy, is valued for its high…
Request A Quote