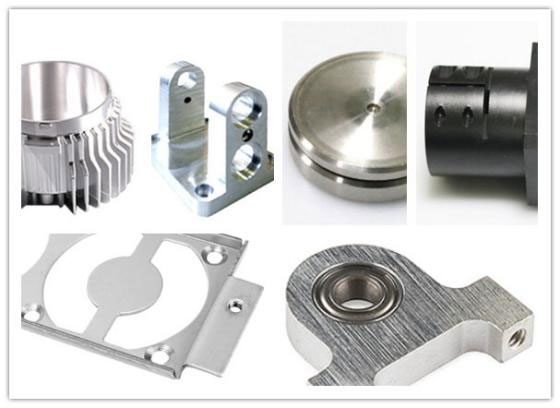
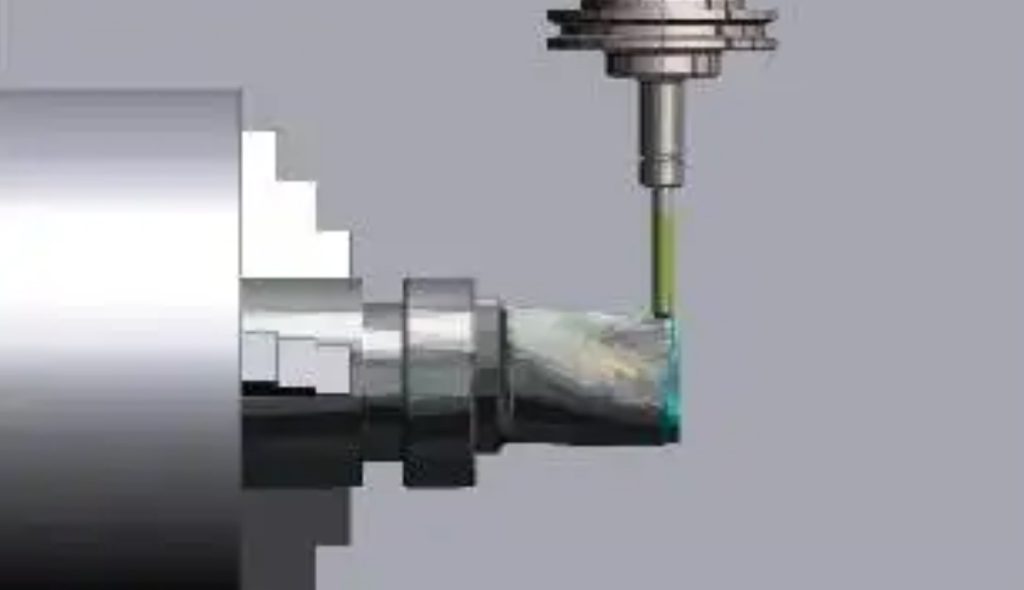
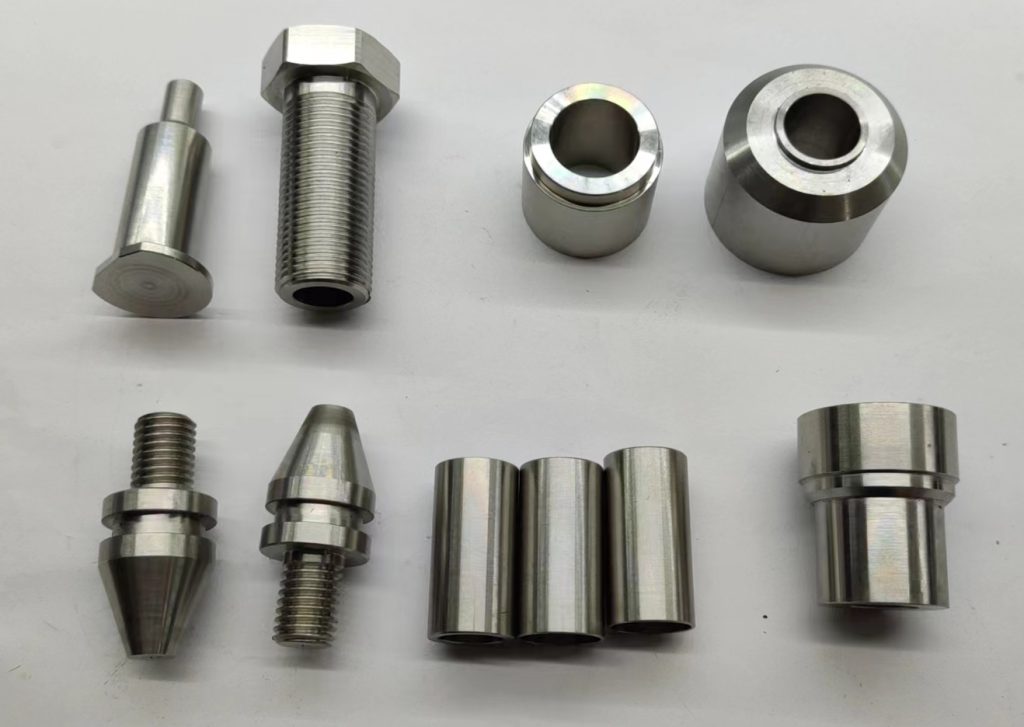
The waste of material has always been a difficult problem in the production of articles. Substantial amounts of material are wasted in various industries, such as aerospace, medical implants, and high-precision tooling; not only that, but the situation also violates the goals of eco-friendliness. Hybrid manufacturing, which connects metal 3D printing and CNC machining together, reveals itself as the right approach for high-waste-factor parts. Manufacturers by co-existing opposite technologies – additive and subtractive, will reduce material waste at least by 50%, and will still be able to provide the demanded accuracy for the crucial parts. In the remaining part of this text, we are going to discuss the amazing outcomes of hybrid manufacturing and why it is considered a new era of B2B operations.

What is Hybrid Manufacturing?
The hybrid manufacturing method is the combination of additive manufacturing and subtractive CNC machining. It is used for making complex parts primarily with metal 3D printing; besides, traditional methods have difficulties in creating such internal geometries and channels. The hard work and special operations, such as the use of machines to fix surfaces, holes, and features that require high precision, are done through the CNC machine.
This dual strategy is the answer to both the hitherto not very flexible CNC model and the insufficiency of the dimensional precision that a 3D printer brings. The scenario gets better if a company combines conventional and additive manufacturing, as they can produce faster, save materials, and have better quality at the same time.
Key Benefits:
- Reduced scrap material compared to fully subtractive machining.
- Ability to produce complex, lightweight designs.
- Enhanced dimensional accuracy through CNC finishing.
How Hybrid Manufacturing Reduces Material Waste
One of the most compelling advantages of hybrid manufacturing is its ability to dramatically cut material waste. Here’s how it works:
1. Additive Manufacturing Minimizes Excess Material
Metal 3D printing implies that only part of the structure is supplemented with material. Traditional CNC milling is different, and it carves out big blocks of metal, while in additive manufacturing, parts are made one layer at a time. As the layers are created one on top of another, the material waste is reduced.
2. CNC Precision Finishing Limits Cutting
The priority of CNC machining in a hybrid workflow is not to cut the whole workpiece roughly, but to work on critical surfaces, holes, and tolerance-sensitive features. In this way, precision is ensured in the area where it is most needed while the volume of material removed is reduced to the minimum.
3. Optimized Internal Structures Reduce Bulk
Hybrid manufacturing offers designers the ability to include lattice structures, hollow channels, and lightweight geometries. Despite the reduced amount of metal, these attributes will still provide strength.
Real-world Impact: The aerospace industry has been able to cut down on waste produced by the parts made using hybrid manufacturing by 50-60%, which in turn means lower costs for raw materials and less energy used for machining and recycling.

Where is Hybrid Manufacturing Used for?
Hybrid manufacturing is particularly valuable in sectors where high precision, lightweight structures, and cost efficiency are critical.
1. Aerospace
Engine components, structural brackets, and cooling channels benefit from the ability to print complex internal features. By combining metal additive manufacturing with 5-axis CNC finishing, aerospace engineers can produce parts that are both lightweight and highly durable.
2. Medical Implants
Custom implants like hip joints, dental fixtures, and spinal devices are feasible for unique patients. The use of hybrid manufacturing elicits the outcomes with the highest quality of surface, material conservation, and tight tolerance criteria, while the waste production is cut down to satisfy the very restricted medical standards.
3. High-End Industrial Molds
It is possible to make complex molds with intricate cooling channels or cavities by using additive manufacturing and then perfecting them by CNC machining. The product will be more durable, and there will be less waste of raw material.
Cost and Sustainability Benefits
Reducing material waste is not only an environmental win—it also delivers substantial cost advantages:
- Reduced raw material expenses: One of the great economies that happens when a company restricts metal material use for the part is the enormous cut in costs of the expensive metals like titanium and nickel alloys.
- Decreased waste handling and recycling costs: Lack of scrap reduces the need for both investment and spending on reprocessing or dumping.
- ESG and green manufacturing goal support: A company can be a sustainability advocate, a corporate image enhancer, and an environmental regulation abider at the same time if it desires to.
The investigations illustrate the potential of hybrid manufacturing to reduce material costs by 50%, at the same time, reduce energy consumption in machining. This is synonymous with increased margins and more effective operational procedures for the purchasing and manufacturing managers.

Key Considerations for Implementing Hybrid Manufacturing
For companies looking to adopt hybrid manufacturing, several critical factors should be considered:
1. Design Optimization
Parts have to be designed in a way that they make the most of 3D printing for intricate forms; even so, they have to be compatible with CNC finishing for the most important surfaces. Smooth design lessens the number of attempts and makes sure the best use of the material.
2. Equipment Selection
Hybrid workflows need both metal 3D printers and high-precision 5-axis CNC machines which are capable of tight tolerance levels to work with.
3. Workflow Planning
A well-defined process—typically additive first, subtractive second—ensures quality, repeatability, and cost-effectiveness. Close collaboration between design, engineering, and production teams is essential.
In Summary
The rise of hybrid manufacturing is a powerful innovation in the production of high-margin parts. By an alliance of metal 3D printing and CNC machining, manufacturers can increase material waste by more than 50%, heighten part precision, and also raise overall manufacturing efficiency. Those sectors like aerospace and medical implants have started to improve their profit, and hybrid workflows were introduced not only as a temporary play, but they are a smart choice for affordable and environmentally friendly production.
Want to see for yourself the benefits of hybrid manufacturing for your production, waste reduction, and component precision? Get in touch with us today to do the talks about the exact solutions, setting up the workflow, and initial equipment recommendations for the next project.

FAQ
Q1: What types of materials can be used in hybrid manufacturing?
Metals such as titanium, stainless steel, aluminum alloys, and nickel-based superalloys are commonly used.
Q2: How much material can actually be saved using hybrid manufacturing?
Real-world applications demonstrate a 50–60% reduction in raw material waste compared to traditional CNC machining.
Q3: Which industries benefit the most from hybrid manufacturing?
Aerospace, medical implants, high-end industrial molds, and precision tooling industries gain the greatest advantage.
Q4: Does hybrid manufacturing require specialized design software?
Yes, CAD/CAM software capable of handling both additive and subtractive processes is essential for workflow optimization.