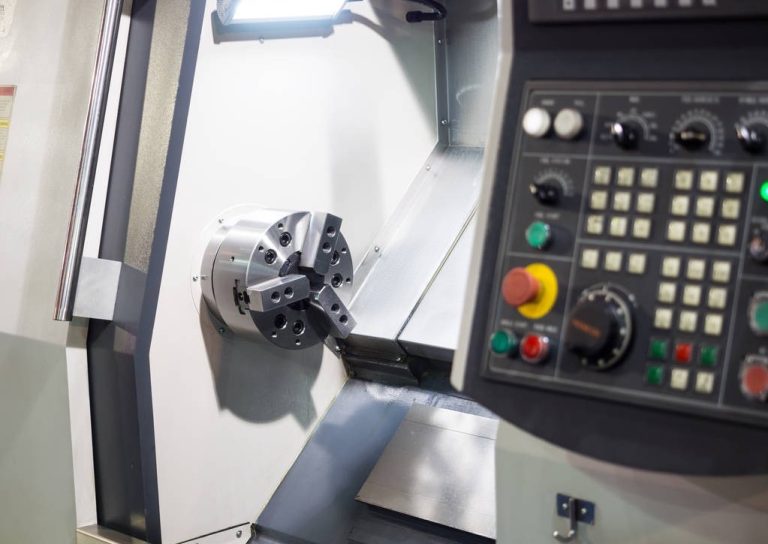
In modern manufacturing, CNC turning plays a critical role in producing round or cylindrical parts with high precision. But just how precise is CNC turning, and what variables influence its accuracy?CNC turning is capable of extremely high precision, especially on machines built for tight-tolerance production. For most industrial applications, it can reliably deliver tolerances within ±0.005 mm, and in specialized cases even tighter. Consistent quality and repeatability make it a go-to process for critical parts.

What is CNC Turning Precision?
CNC turning precision refers to the machine’s ability to produce parts that adhere closely to the specified dimensions, tolerances, and surface quality set in the design. Unlike general-purpose turning, CNC lathes are computer-controlled, enabling consistent, repeatable results across high or low-volume production.
In high-end environments, CNC turning can achieve tolerances as tight as ±0.002 mm (±0.00008 inch), making it suitable for applications where micron-level accuracy is critical.
What Affects CNC Turning Precision?
- Machine Quality – High-end lathes and Swiss-type turning centers provide better tolerances.
- Tool Condition – Sharp, well-maintained tools reduce vibration and maintain tighter dimensions.
- Material Type – Harder materials may require slower feeds to maintain accuracy.
- Thermal Expansion – Heat can slightly alter part dimensions, especially in long runs.
- Chuck and Fixture Setup – Precision workholding minimizes part movement.
Typical Precision of CNC Turning
- Standard Tolerances: ±0.01 mm to ±0.05 mm (±0.0004 in to ±0.002 in)
- High-Precision Tolerances: ±0.002 mm to ±0.005 mm (±0.00008 in to ±0.0002 in)
- Surface Roughness: As low as Ra 0.4–1.6 µm depending on tool and speed
Key Dimensions of CNC Turning Precision
| Dimension | Description | Typical Performance |
| Dimensional Tolerances | The allowable deviation from the part’s specified dimension, depending on machine type and part complexity. | – Standard: ±0.01 – ±0.05 mm- High-Precision: ±0.002 – ±0.005 mm- Swiss-Type: even tighter |
| Roundness & Concentricity | Critical for rotating parts, ensures the component remains balanced and aligned on its axis. | Roundness achievable within 0.001 mm |
| Surface Finish | Defines the texture of the part’s surface, important for friction, fit, and aesthetics. | Ra 0.4 – 1.6 µm, depending on tool, speed, and material |
| Repeatability | The machine’s ability to produce identical parts across multiple production runs, ensuring consistency. | Within ±0.002 mm for high-end machines |
CNC Turning Precision by Industry
| Industry | Typical Tolerance Range | Application Examples |
| Aerospace | ±0.002 – ±0.005 mm | Engine shafts, bushings, precision sleeves |
| Medical Devices | ±0.003 – ±0.01 mm | Surgical tools, implants, dental components |
| Automotive | ±0.01 – ±0.02 mm | Gears, pistons, steering components |
| Electronics | ±0.005 – ±0.01 mm | Connectors, pins, small housings |
How to Maximize Precision in CNC Turning
To achieve optimal results from CNC turning, consider these best practices:
- Use rigid tooling and properly maintain cutting edges
- Keep machines calibrated regularly
- Control shop temperature and humidity to reduce thermal deviation
- Program slow and steady cuts for tight-tolerance work
- Choose the right material-grade for stability during machining
Final Thoughts
CNC turning offers a powerful combination of speed, repeatability, and micro-precision, making it ideal for producing high-tolerance, high-quality cylindrical parts. From aerospace components to custom medical implants, CNC turning delivers unmatched precision when properly applied.CNC Turning Service
JTR Machine can use the CNC turning process to make parts or product prototypes and mass-produce them. General threading, and CNC machining of round parts including shafts, worms, and balls.