High-precision construction is necessary to continue developing new medical devices, producing new aerospace devices, and manufacturing advanced medical devices. Compact and complex devices that demand high levels of safety require CNC turning to meet the necessary production levels. Consistency in quality and unchanged production levels in CNC turning’s primary post-processing construction include plating, coating, and anodising to create CNC machined pieces.

CNC Turning for High-Precision Applications
1. Importance of High Precision
There are certain industries, such as medical and aerospace, that have regulatory and safety guidelines that are unyielding. The medical field has to ensure that medical implants fit the human body. In aerospace, fasteners and hydraulic parts have to withstand extreme pressures as well as extreme temperatures. Equipment that is used in these aerospace industries has to be high-end and must remain stable in its dimensions in order to perform accurate measurements and/or operations. These parts are extremely necessary; therefore, every detail has to be machined with extreme precision. There is no room for even the slightest error; otherwise, they will fail, it will result in a loss of lifespan, or regulations will not be achievable.
2. Capabilities of Modern CNC Turning Service
CNC turning services nowadays utilise modern technology such as multi-axis lathes and turn-milling centres that have the ability to create complex geometries with a single setup. With automated tool supervision, these computers attain high precision at a tolerance of (±) 0.005. Not only are these computers consistent throughout the manufacturing process, but they also save time and have the ability to scale production.
3. Custom CNC Turning for Multifunctional Components
If standard components do not meet functional, dimensional, or material requirements, custom CNC turning becomes necessary. Certain industries require custom parts with unique geometries, for example, precision internal channels, small shafts, specific thread designs, or complex shapes. Custom machining achieves specific performance specifications, such as improved fluid dynamics or higher mechanical strength for ergonomic designs. This is especially important for components such as surgical connectors, aerospace bushings, and shafts for precision instruments.
CNC Turning Materials: Metals, Alloys, Polymers
1. Common High-Performance Materials
Alloyed Titanium is usually used for medical implants, and for its biocompatibility, strength, and corrosion resistance. For surgical instruments, stainless steels like 316L and 304 are used due to their durability and ability to be sterilised. In aerospace, and for their lightweight construction, aluminium alloys like 6061 and 7075 are used due to their thermal and mechanical properties. Other alloys are used for their easy machinability.
2. Engineering Plastics in Lathe Turning Plastic Applications
In electronics and medical lathe applications, engineering plastics like PEEK, PTFE, Delrin, ABS, Nylon, and PC are becoming more important. With their lightweight and low friction, along with their chemical resistance and electrical insulating attributes, they are used for surgical instrument handles, sensor housings, laboratory fittings, and parts for high-end electronics. PEEK is used for its high temperature and performance in relation to dimensional stability.
3. Material Challenges and Machining Considerations
Different CNC turning material categories present their unique challenges that need to be accounted for. Titanium tends to heat up. It also requires steady cutting tools. Stainless steel can be problematic as well since it can contribute to rapid tool wear. Plastics can also be added to the list, as they can warp. They can also melt and produce burrs that shouldn’t be there if they aren’t machined correctly. It is the manufacturer’s job to determine the most suitable tooling, cutting speeds, refrigerants, and chip removal for the operation that needs to be performed to retain quality and protect surface detail and order, especially if the surface integrity of the material is important.
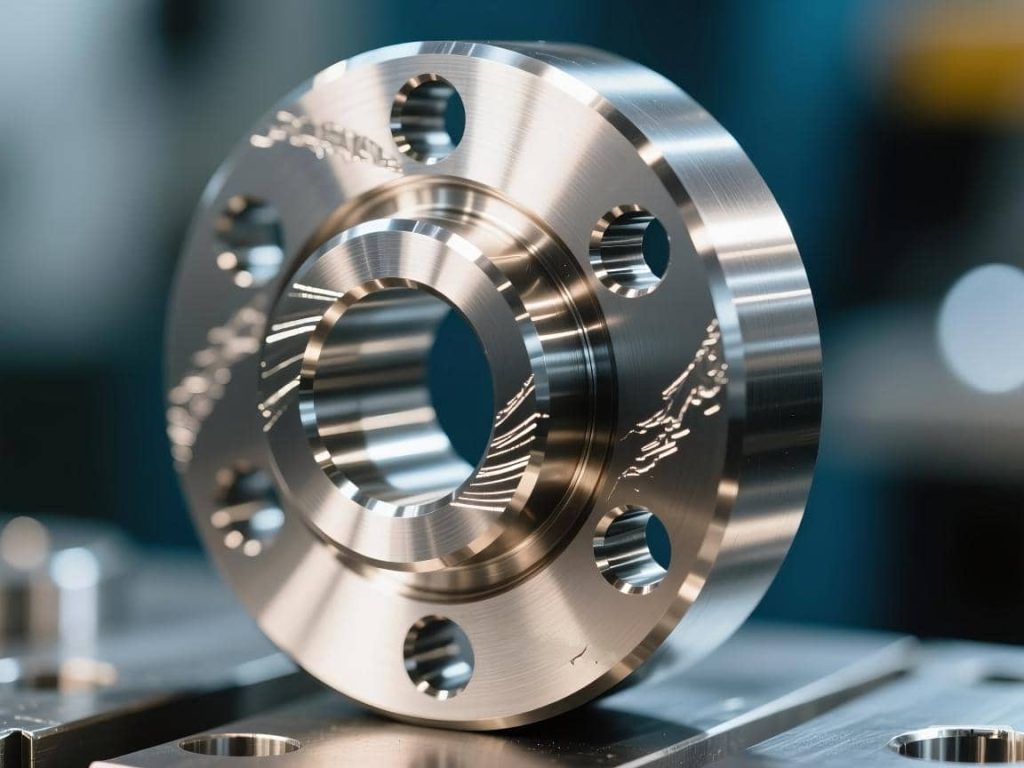

CNC Turning Components for Medical, Aerospace, and High-End Devices
1. Medical Components
Examples of devices produced using CNC turning in medicine include bone screws, orthopedic pins, dental implants, parts for endoscopic systems, connectors for surgical tools, and housings for surgical instruments. Products in this field must be biocompatible and have very smooth surfaces. They also must have micro precision. Custom CNC turning is often needed for specific anatomical and procedure requirements.
2. Aerospace Components
CNC turning is also used in the aerospace field, where systems need extreme and high precision. Parts needed include brackets, bushings, structural spacers, and fasteners. Additionally, parts are needed for the hydraulic systems and for the engines. These pieces need to be able to manage great stress and temperature.
3. High-End Equipment Components
CNC precision metrology, laboratory, and optical systems all depend upon turned CNC wood parts for proper stable alignment. These devices and systems require the turning of sensor housings and optical mounts to very tight tolerances with low roughness to control drifting.

The Importance of Surface Finishing: Anodizing, Plating, Coating
1. Importance of Surface Finishing
When machining is done on a part, surface finishing on the part is a must to obtain maximum improvement to the defect and performance and even get some improvement to the visual appeal of the part. Some of the traits improved by finishing for certain industries, like medical and aerospace, are corrosion resistance, ability to sterilise, electrical conductivity, wear resistance, and even fatigue strength. Surface treatment helps support that CNC turning components not only fit as intended, but also perform satisfactorily during adverse conditions.
2. Anodizing
Anodising is a common practice for aluminium and titanium components. This is because anodising is an electrochemical process that thickens the oxide layer naturally on the surface of the metals. This creates an anodised surface which is hard and wear resistant. It is also resistant to corrosion. Medical tools benefit from colour anodising because they can be identified quickly and easily compared to non-processed medical tools. Aerospace parts benefit from anodising as well because they improve anodised parts that undergo abrupt climate changes.
3. Plating
Some of the functional advantages of the plating methods are: nickel plating, chrome plating, and gold plating. Some functional benefits of nickel plating would be improved corrosion resistance and improved wear resistance. Some common functional benefits of chrome plating would be improved surface hardness of the part. If a part is gold plated, it is usually for electrical parts, and the purpose is to improve the electrical conductivity of the part, especially for the sensors and other electronic equipment. There are finishing options for equipment, and they become more important for equipment aimed at high-end consumers.
4. Coating (Ceramic, PVD, PTFE, Diamond-Like Carbon)
High-tech coatings reduce friction, improve wear resistance, increase fatigue strength, and improve thermal stability. PTFE coatings are used on medical devices that need to slide easily. For aerospace and other high-stress uses, DLC and ceramic coatings are preferred.
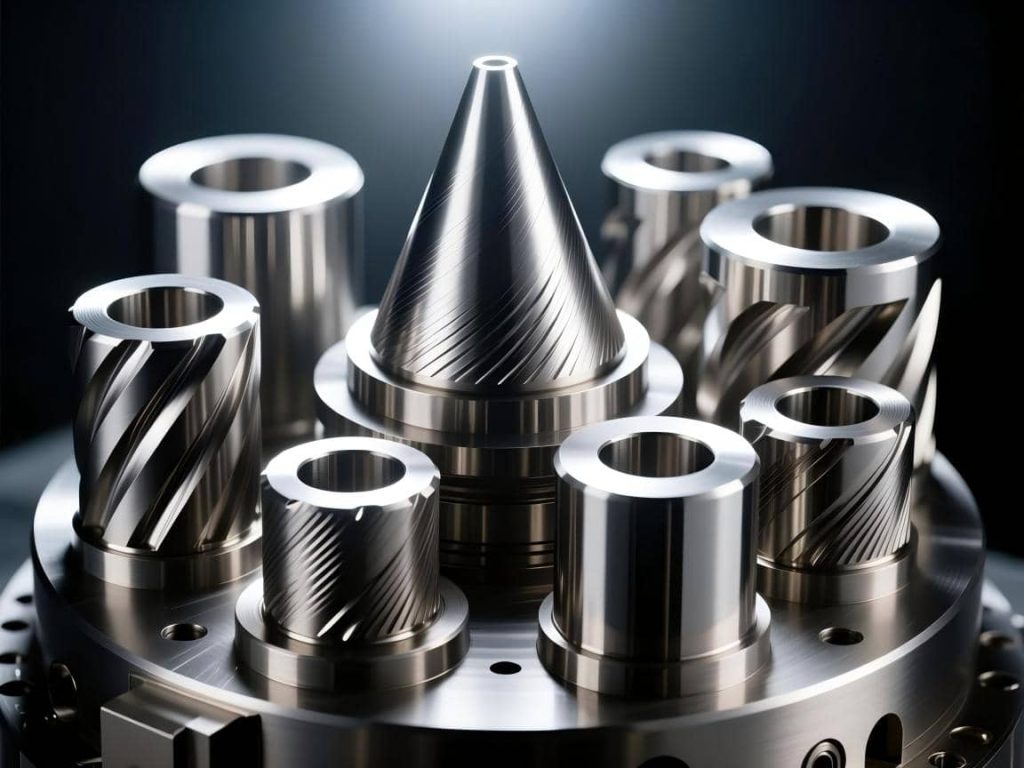

Combining Advanced Finishing with Precision Machining
1. Finishing Is Never First
Before any finishing processes like anodising, plating or coating can occur, high-precision machining is required. Engineers need to consider any possible changes to dimensions that can occur due to changes in thickness from finishing processes. Critical fits need to remain accurate after finishing; no changes can be tolerated.
2. Manufacturing Workflow Optimization
Modern workflows use a combination of CAD/CAM systems, real-time simulation, and automated measurement. Surface quality is improved from toolpath optimisation and in-process inspections, like a CMM or optical scanning, to gather measurements to ensure finishing is completed accurately.
3. Quality Verification and Compliance
In the medical and aerospace fields, certifications like ISO 13485 and AS9100 must be complied with. There are industry standards that must be met, and these include required surface roughness levels like Ra < 0.8 µm for medical instruments. Final quality inspections to ensure that the product will meet the safety and performance requirements of its use and durability are completed.
Conclusion
In the manufacture of medical devices, aerospace systems, and high-end instrumentation, high precision CNC turning, along with advanced finishing techniques like anodising, plating, and coating, is crucial. Performance of the component in the end will be influenced by every step taken, starting from the CNC turning material to be used, to the machining of engineering plastics, to the application of specially designed surface treatments. As industries continue to move towards higher accuracy and increased reliability, along with miniaturisation, custom CNC turning will continue to be crucial for the production of complex, high performing components.










