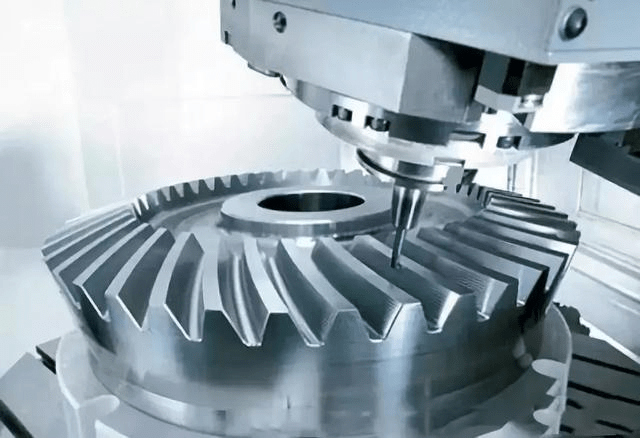
For procurement managers in the aerospace industry, few components carry as much cost, risk, and strategic importance as the turbine disk. As a core rotating component in aero engines, the turbine disk operates under extreme temperature, stress, and fatigue conditions, leaving zero tolerance for defects.
By 2026, turbine disk manufacturing has entered an era defined by AI-assisted 5-axis machining for turbine disk manufacturing, digital inspection, and hybrid production methods. These advances are not just engineering upgrades—they directly affect supplier qualification, total cost of ownership (TCO), lead times, and compliance risk.
The contemporary technologies in the production of turbine disks are outlined alongside the equipment that is used and how they are utilized in the production process.

Near-Net Shape Forming: Cutting Material Cost at the Source
1. Powder Metallurgy and HIP for Cost-Efficient Superalloy Use
Traditional turbine disk production relied on machining from solid forged billets, resulting in massive material waste—an unacceptable cost when working with nickel-based superalloys.
The modern near-net shape powder metallurgy turbine disk process addresses this issue at the earliest stage. Fine metal powders are consolidated using Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP), producing dense preforms that closely match the final geometry.
Procurement value:
- Reduces raw material waste by 30–50%
- Stabilizes pricing exposure to volatile superalloy markets
- Improves batch-to-batch consistency, reducing rejection risk
For sourcing teams, suppliers with in-house powder metallurgy and HIP capability typically offer more predictable cost structures and shorter material lead times.
2. Hybrid Manufacturing with DED for Design Flexibility
In advanced programs, hybrid manufacturing DED for aerospace turbine components is increasingly used. Laser Directed Energy Deposition (DED) builds additional material only where needed, such as blade root regions.
Why this matters to buyers:
- Lower machining allowance means reduced CNC hours
- Faster design iteration without new forging tools
- Improved responsiveness to engineering change orders (ECOs)
From a procurement standpoint, hybrid manufacturing capability signals a supplier’s long-term adaptability rather than dependence on fixed tooling.
AI-Assisted 5-Axis Machining: Predictable Cost in a Difficult Process
1. Trochoidal Milling for Superalloy Machining Efficiency
Machining nickel-based superalloys is notoriously expensive due to rapid tool wear and heat buildup. Modern suppliers rely on trochoidal milling for nickel-based superalloy machining, using high-speed, low-engagement toolpaths.
Procurement impact:
- Lower tooling consumption
- Reduced unexpected downtime
- More stable per-part machining cost
For buyers, this translates into more reliable quotations and fewer cost overruns during serial production.
2. AI Monitoring and Adaptive Spindle Control
Leading manufacturers now deploy real-time sensors and AI systems to monitor vibration and chatter during cutting. When abnormal frequencies are detected, the system automatically adjusts spindle speed using Spindle Speed Variation (SSV).
Why procurement should care:
- Prevents catastrophic scrap of high-value near-net blanks
- Protects delivery schedules from sudden quality failures
- Demonstrates process maturity during supplier audits
Suppliers using AI-assisted machining are typically better positioned to meet long-term contract commitments.

Fir-Tree Slot Machining: Where Supplier Capability Truly Shows
1. Why Fir-Tree Slots Are High-Risk Features
The fir-tree (or “Christmas tree”) slots connecting blades to the disk experience extreme cyclic stress. Even microscopic defects can cause premature failure.
From a sourcing perspective, this operation often separates qualified aerospace suppliers from general CNC machining service factory.
2. WEDM vs. Traditional Broaching
Historically, broaching was standard—but it introduces high cutting forces and residual stress. In contrast, WEDM vs broaching for turbine disk slot machining is now a key evaluation topic.
WEDM advantages for procurement:
- Lower mechanical stress on the disk
- Better dimensional consistency across batches
- Reduced rework and inspection failures
Choosing suppliers that favor WEDM or advanced EDM methods significantly lowers long-term reliability risk.
3. Ultrasonic-Assisted Machining for Surface Integrity
Some suppliers further enhance quality using ultrasonic-assisted machining of turbine disk fir-tree slots, where high-frequency vibrations reduce cutting resistance.
Procurement takeaway:
- Improved surface finish without secondary polishing
- Higher fatigue life margins
- Strong alignment with aerospace OEM qualification standards
Digital Inspection and In-Situ Metrology: Reducing Quality Escapes
1. In-Situ Measurement Without Removing the Part
Modern facilities use digital inspection and in-situ metrology for aerospace components, measuring critical dimensions directly on the machine.
Benefits for sourcing teams:
- Fewer handling-related errors
- Faster inspection cycles
- Higher first-pass yield
This directly improves on-time delivery performance, a key KPI in procurement contracts.
2. AI-Driven Non-Destructive Testing
Automated fluorescent penetrant inspection combined with AI vision systems now detects micron-level surface cracks and generates a digital part passport for traceability.
Why this matters:
- Stronger compliance documentation
- Reduced risk of downstream recalls
- Simplified supplier quality audits

Surface Enhancement and Heat Treatment: Protecting Lifecycle Value
1. Shot Peening for Fatigue Life
Shot peening and vacuum heat treatment for turbine disk fatigue life are essential post-processing steps. Shot peening introduces compressive residual stress, dramatically extending service life.
Procurement relevance:
- Longer component life reduces aftermarket liability
- Supports OEM warranty and safety requirements
2. Vacuum Heat Treatment for Stability
Vacuum furnaces ensure precise aging and stress relief without oxidation.
For buyers:
- Better dimensional stability over time
- Lower risk of in-service distortion
- Strong indicator of aerospace-grade infrastructure
Traditional vs. 2026 Turbine Disk Manufacturing: Process Comparison
To clearly illustrate how turbine disk manufacturing has evolved from experience-driven workflows to intelligent, closed-loop production, the following table compares traditional processes with AI-driven manufacturing approaches adopted in 2026 from a process engineering perspective.
| Process Dimension | Traditional Manufacturing | 2026 AI-Driven Manufacturing | Process Engineering Impact |
| Starting Material | Solid forged billet with large machining allowance | Near-net shape powder metallurgy + HIP | Significant reduction in material waste and rough machining time |
| Material Utilization Rate | Low (high chip volume, scrap risk) | High (minimal excess material) | Lower raw material cost, more predictable process planning |
| Manufacturing Strategy | Subtractive machining dominant | Hybrid manufacturing (DED + machining) | Upstream complexity reduces downstream machining burden |
| Rough Machining Method | Conventional pocket milling | Trochoidal milling with AI optimization | Improved thermal control and tool life stability |
| Machine Tool Control | Fixed parameters, operator experience driven | AI-assisted 5-axis machining with real-time feedback | Closed-loop control minimizes chatter and unexpected failure |
| Chatter & Vibration Management | Conservative cutting parameters | Sensor-based detection with SSV adaptive control | Enables aggressive yet stable cutting strategies |
| Fir-Tree Slot Machining | Mechanical broaching | Multi-axis WEDM + ultrasonic-assisted machining | Lower residual stress and improved surface integrity |
| Cutting Forces | High mechanical load | Near-zero force (EDM) or reduced force (ultrasonic) | Reduced risk of microcrack initiation |
| Dimensional Verification | Offline CMM inspection | In-situ metrology on machine | Faster feedback and elimination of re-clamping errors |
| Surface Defect Detection | Manual or semi-automatic NDT | AI-based digital inspection systems | Higher detection sensitivity and consistency |
| Residual Stress Control | Post-process correction | Process-embedded stress minimization | Improved dimensional stability during service |
| Surface Enhancement | Shot peening as a corrective step | Shot peening as a life-extension design step | Fatigue life optimized by design, not by rework |
| Heat Treatment | Atmosphere furnace | Precision vacuum heat treatment | Superior microstructure stability and cleanliness |
| Process Traceability | Batch-level documentation | Digital part passport (component-level) | Full lifecycle traceability and compliance readiness |
| Production Lead Time | Weeks to months | Days to weeks | Faster response to design changes and demand shifts |
| Scrap Rate | Relatively high for superalloys | Near-zero with digital twin validation | Predictable yield and lower financial risk |
| Overall Process Philosophy | Experience-driven, reactive | Data-driven, predictive, and adaptive | Process engineers shift from firefighting to optimization |

Conclusion: What Procurement Managers Should Look for in 2026
For procurement professionals, turbine disk sourcing is no longer just about unit price. The integration of AI-assisted 5-axis machining, near-net shape powder metallurgy, WEDM slotting, and digital inspection fundamentally reshapes supplier risk profiles.
Key sourcing criteria in 2026 should include:
- Proven AI-driven machining and monitoring
- In-house powder metallurgy or hybrid manufacturing capability
- Advanced slot machining (WEDM / ultrasonic-assisted)
- Fully digital inspection and traceability systems
CNC machining services manufacturers that make investments in these tools that are able to come up with the lowest cost of ownership, and, which is of significance, increased liability of operations or sustainable programs over a significant period of time.