Automotive manufacturing once relied entirely on molds and assembly lines, churning out standardized parts in high volumes. This approach was costly, time-consuming, and left little room for customization.
Now, 3D printing is entering the industry as a game-changer. It enables on-demand part production and makes small-batch manufacturing economically viable. The technology is already at work—from high-end super cars to everyday vehicles.
This article explores how 3D printing is revolutionizing automotive manufacturing. It demonstrates the technology’s role in enabling mass customization, reducing costs, and driving innovation. Ultimately, 3D printing is forging a new era of agile, intelligent automotive production.
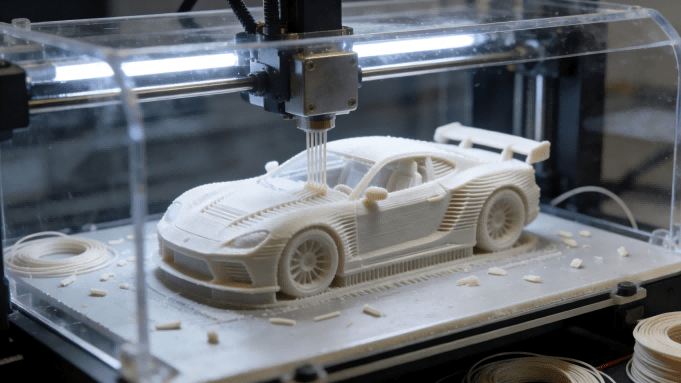
3D Printing: The Game-Changer Redefining Automotive Manufacturing
For over a century, the automotive industry has been ruled by the economics of scale. Massive investments in molds, dies, and assembly lines made mass production efficient, but rendered customization costly and small-batch production nearly unthinkable.
Today, a quiet revolution is underway, challenging these foundational principles. 3D printing, or additive manufacturing, is emerging not merely as a novel tool, but as a fundamental game-changer.
By enabling the cost-effective creation of complex, on-demand parts—from bespoke interior elements to performance components—it is dismantling the traditional barriers of design, production, and supply chains. The question is no longer if 3D printing will impact automotive manufacturing, but how profoundly it will reshape the very DNA of the industry.
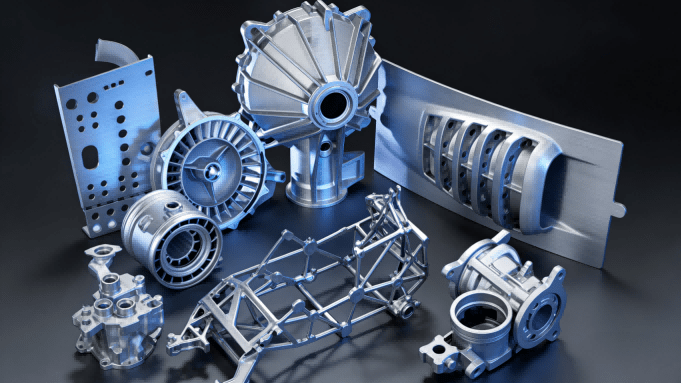
The Core of Innovation — Four Key Application Breakthroughs of 3D Printing in the Automotive Industry
3D printing technology has progressed beyond proof-of-concept into every phase of the automotive life cycle—from design and manufacturing to after-sales and business models. Its value lies not just in creation, but in solving intractable problems of traditional processes.
The following four application areas are actively shaping the blueprint for tomorrow’s automotive manufacturing.
Design & Development: The Innovation Accelerator, Turning “Months” into “Days”
In the traditional workflow, testing the design of a new component could take months and require hundreds of thousands in tooling investment. 3D printing has completely redefine this workflow.
Rapid Prototyping & Iteration: Engineers can obtain physical models within hours for fit-and-assembly checks, aerodynamic testing, and even functional validation. This compresses the “design-test-optimize” cycle exponentially, dramatically accelerating the pace of new vehicle development.
Functional Integration & Topology Optimization: Compared with traditional methods, 3D printing enables design consolidation, integrating several functions into a single, complex part. This reduces weight, enhances performance, and minimizes potential points of failure.
Iconic Case Study: A leading German automaker used 3D printing to produce a fully functional water pump prototype for a new engine. The process, which would have taken 10 weeks and required expensive tooling traditionally, was completed in 2 weeks at low cost, enabling rapid performance tuning.
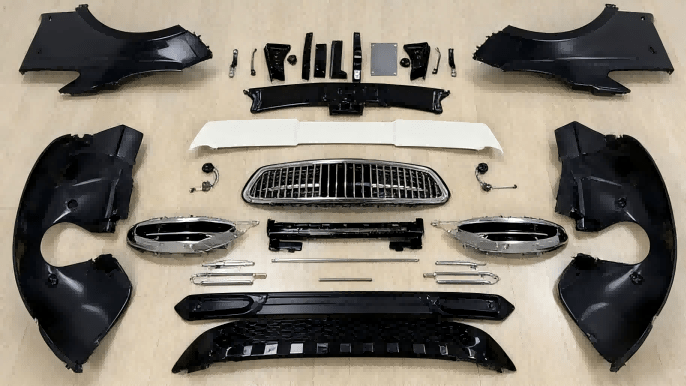
Production & Customization: The Bridge to Low-Volume and Bespoke Manufacturing
Customized End-Use Parts: From personalized seat cushion inserts (with tailored firmness zones) to custom shift knobs and lightweight brake calipers, 3D printing enables mass customization at viable costs. It allows manufacturers to offer premium, individualized options that were previously impractical.
Low-Volume & Legacy Support: 3D printing creates a “digital inventory”—storing part designs instead of physical stock. Parts can be printed on-demand, as exemplified by the restoration of rare classics like the Porsche 959, ensuring longevity without massive warehousing costs.
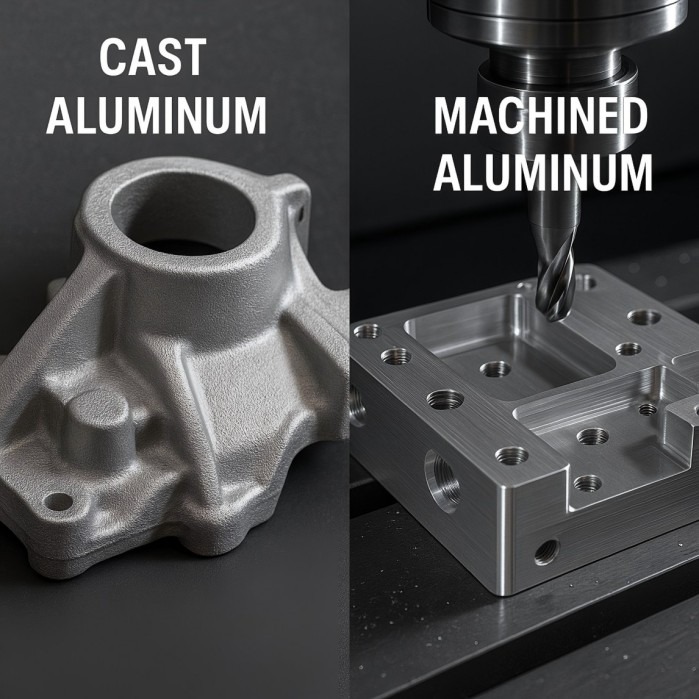
Lightweighting for Performance: By using advanced materials like titanium or carbon-fiber-reinforced polymers, 3D printing produces parts that are stronger and significantly lighter than their cast or machined counterparts. This directly contributes to improved fuel efficiency, battery range in EVs, and enhanced vehicle dynamics.
Supply Chain & Tooling: Building Resilience and Efficiency
3D printing introduces unprecedented flexibility and resilience into the traditionally rigid automotive supply chain.
Digital Warehousing & On-Demand Production: Producing parts locally and on demand lowers inventory costs, minimizes logistics emission and mitigates global event risks. The shift from physical stockpiles to digital files is now operational at major automotive companies.
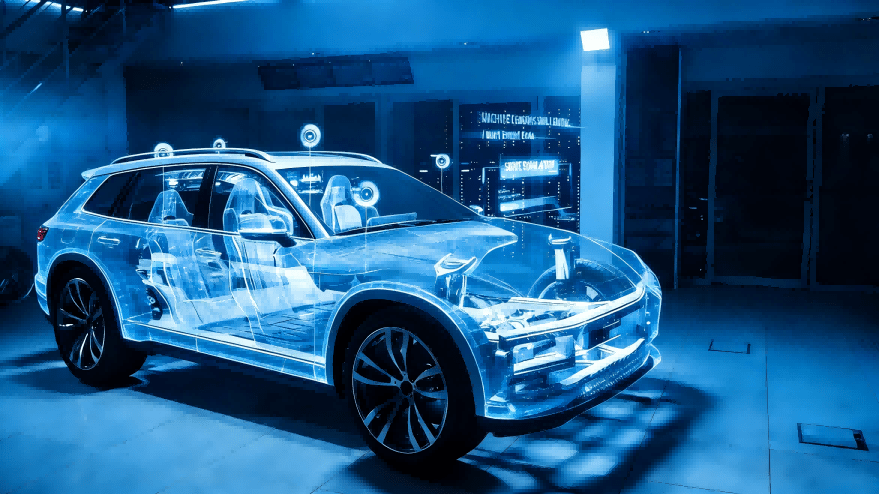

The Future on the Horizon: Next-Generation Mobility
The ultimate promise of 3D printing points toward a redesigned vehicle architecture and ownership model.
Visionary projects are exploring printed multifunctional monolithic structures, drastically reducing part count and assembly complexity; additive manufacturing promotes material efficiency, using only the necessary material with minimal waste. It also opens the door to using recycled and bio-based polymers, supporting the industry’s transition toward a circular economy and greener production cycles.
Navigating the New Era of Convergent Innovation
3D printing has moved from the showroom to the factory floor. It is a powerful enhancement to traditional automotive manufacturing, and serves as a key catalyst for agile production and personalized solutions.
The future of the industry lies in hybrid manufacturing. This convergence of scale and flexibility will define the next era of automotive competitiveness and innovation.